The English Grammar Tenses
Collection
Welcome to the English Grammar Tenses – The Ultimate Resource!
One of the easiest ways to teach and learn grammar is through
stories.
Click Here for Step-by-Step Rules, Stories and Exercises to Practice All English Tenses

So we at Really Learn English made this huge collection of stories
and exercises available for you, completely free of
charge.
You can read the stories online, download the story PDF
files, print and use them by yourself or with your students,
and check the answers using the answer key.
All we ask in return, is
that if you find this resource useful, please
link to it and share it with your students, colleagues, and anyone else
who may benefit from it. You can link to this page from your website,
blog, Facebook, Twitter, LinkedIn, Google+, etc.
Thanks for your support!
What does TENSE Mean?
A tense is a form of the verb which shows
the time at
which an action happens.
It comes from the Latin word «tempus», which means
«time».
Click here for the full
article on what tense is.
Please share
this page with others:
Table of
Contents
| Aspect | Time | ||
| Present | Past | Future | |
| Simple | Simple Present | Simple Past | Simple Future |
| Progressive (Continuous) |
Present Progressive | Past Progressive | Future Progressive |
| Perfect | Present Perfect | Past Perfect | Future Perfect |
| Progressive + Perfect |
Present Perfect Progressive |
Past Perfect Progressive | Future Perfect Progressive |
Simple
Present
The Simple Present
is a form of the verb that shows the action or state happens in the
present.
For example:
Lisa dances
every day.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the simple present and how
to use it.
Simple Present Story
1

Who is he? Where is he? What
does he do?
Hank is a cowboy. He lives on a farm. He has a horse named Ginger.
Hank loves Ginger. He rides Ginger every day. Sometimes they walk
slowly, and sometimes they run fast. They always have a good time.
Ginger
is Hank’s horse. She is light brown. Her tail and mane are dark brown.
She is three years old. She lives in the stable by the house.
Ginger
waits for Hank every morning. She enjoys their time together. Often,
Hank gives her apples. After long rides, Hank always washes and brushes
Ginger. He usually brushes her tail. Then he gives her food and fresh
water. Ginger loves Hank.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Present Story 1.
Simple Present Story
2
Who are they? Where are they?
What do they do?
Stacy is a singer. She loves to sing. She is in a band. She sings
in the band. She is the lead singer. Sometimes she plays the piano.
Chad
is Stacy’s boyfriend. He is also in the band. He stands next to Stacy.
He plays the electric guitar. Sometimes Chad sings with Stacy.
Dean
is Chad and Stacy’s friend. He is also in the band. He stands next to
Chad. He plays bass guitar. Dean does not sing. He does not like to
sing.
The band practices three times a week. They mostly perform
at nightclubs. Sometimes they sing at weddings. They are a very good
band.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Present Story 2.
Simple Present Story
3
Who is he? Where is he? What
does he do?
Jim Sullivan likes music. He plays many instruments. He plays the
piano, clarinet, saxophone, trumpet, guitar, and bagpipes. The bagpipes
are his favorite instrument to play. Not very many people play the
bagpipes.
Jim plays the bagpipes for celebrations. He also
plays the bagpipes in parades. The audience listens to the bagpipes.
They clap for Jim. They enjoy the music of the bagpipes.
Jim
also teaches people how to play the bagpipes. He gives lessons to
children and adults. He teaches them the history of the bagpipes. He
teaches them how to play music with the bagpipes. Jim is a good teacher.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Present Story 3.
Simple Present
Story 4 
Who is he? Where does he
live? What does he do?
Robert Hughes lives in Atlanta, Georgia. He lives with his wife,
Patricia. They live with their two children, Sam and Lana. Robert loves
his family.
Robert works as a police officer in Atlanta. He
likes his job. He is a good police officer. Robert is a police officer
because he likes to help people.
Robert protects the citizens of Atlanta. He solves crimes and catches
criminals. He keeps the citizens safe.
Sometimes he visits the schools. He talks to students. The students
like Robert. Officer Robert Hughes is a hero in Atlanta.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Present Story 4.
Present
Progressive
The Present Progressive
(Continuous) is a form of the verb that shows the action
or state is in progress (continues) in the present.
For example:
Lisa is dancing
right now.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the present progressive and
how to use it.
Present
Progressive Story 1
Who are they? Where are they?
What are they doing?
Now Janet is in her house. She is sitting on a wooden chair. She is
holding a coat. She is fixing it.
James is Janet’s husband. He is sitting in front of her. He is fixing
clothes too.
Elizabeth
is sitting next to James. She is Janet’s sister. Right now she is
helping Janet and James. They are working together. They are fixing
clothes.
At this moment a man is coming in. He is wearing dark clothes. He is
carrying a pile of clothes. They are all working very hard.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Progressive Story 1.
Present
Progressive Story 2
Who are they? Where are they?
What are they doing?
Right now, it is Monday morning. Mike and Tina are at home. They are
sitting at a table. They are eating breakfast.
At
this moment, Tina is drinking coffee. She is eating a pastry. She is
sitting across the table from Mike. She is talking to Mike.
Mike is Tina’s husband. He is sitting at the table with Tina. He is
also drinking coffee. Mike is listening to Tina.
After breakfast, Mike and Tina are leaving for work. They work in the
city. They are riding the bus to work.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Progressive Story 2.
Present
Progressive Story 3
Who are they? Where are they?
What are they doing?
Now the children are at school. Amy is sewing. She is practicing. She
is sitting on a bench. She is sitting near Timmy.
Timmy is at school too. Timmy is studying. He is sitting behind his
desk. He wishes he could play with the other children.
John
and Susan are also at school. They are playing outside. They are
picking flowers for their teacher. John is carrying his hat. Susan is
wearing a bonnet.
At this moment, Sarah is walking by the door. She is helping the
teacher. She is carrying textbooks to the shelf.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Progressive Story 3.
Present
Progressive Story 4
Who are they? Where are they?
What are they doing?
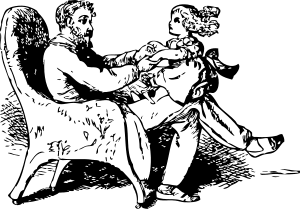
Today, Abby is visiting her grandparents. She loves her
grandparents. At this moment, she is sitting on her grandfather’s knee.
She is listening to a story. She is smiling. She loves her
grandfather’s stories.
Jacob is Abby’s grandfather. He loves his
granddaughter. Right now, he is telling her a story. He is holding her
on his knee. He is holding her hands. They are sitting in the living
room.
Sarah is Abby’s grandmother. At this moment, Sarah is
standing in the kitchen. She is baking cookies for Jacob and Abby. She
is also listening to Jacob’s story.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Progressive Story 4.
Present
Perfect
The Present Perfect
is a form of the verb that shows the action or state was complete
before the present.
For example:
Lisa has danced
already.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the present perfect and
how to use it.
Present
Perfect Story 1
Who are they? What have they
done?
What has happened?
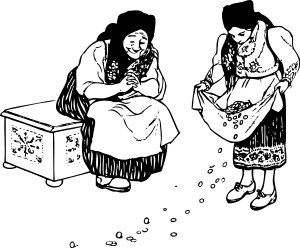
Linda
has
just walked outside with Grandmother. She wears an apron. So far, she
has
finished cleaning and washing. She has also gathered seeds and crumbs.
Now
Linda
and Grandmother are outside. Linda has just dropped some seeds on the
ground to
feed the birds. The birds have not come yet.
Recently,
Grandmother has moved in with Linda’s family. She now enjoys living
with them.
Grandmother
has already sat down on the bench. She also wears an apron. She has
just
finished cooking.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Perfect Story 1.
Present
Perfect Story 2
Who is she? What has she
done? What has happened?
Recently, it has snowed in Maria’s town. In the last week, it has
snowed three times. Maria has always loved the snow. She has played in
the snow many times before.
Maria’s dog, Sparky, has never played in the snow. This is Sparky’s
first snow. He has not felt the cold yet.
Maria
has just received a new sled for Christmas. She puts on her warm
clothes and snow boots. She pulls the sled up the hill. Sparky has run
outside with Maria. Sparky has followed Maria up the hill. He feels
good!
Maria has finally reached the top. She sits on her sled.
She rides down the hill. Sparky runs beside the sled. They have finally
reached the bottom. Sparky has followed Maria all the way down the
hill. Sparky has decided that he likes the snow too!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Perfect Story 2.
Present
Perfect Story 3
Who are they? What have they
done?
What has happened?
Roger and Melinda have owned their sailboat for 10 years. During
that time, they have sailed together many times. They have sailed to
lots of places.
They have sailed on the Pacific Ocean. They have
also sailed on the Atlantic Ocean. They have even sailed around the
Gulf of Mexico twice. However, they have never sailed on the Arctic
Ocean or Indian Ocean.
In the last year, Roger and Melinda
have sailed around the Hawaiian Islands and across the Hudson Bay.
Roger and Melinda love to travel in their sailboat!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Perfect Story 3.
Present
Perfect Story 4
Who is he? What will he have
done?
What will have happened?
Mable Jones lives in Florida in the United States. Her
grandchildren live in London, England. They have lived in London for 3
years. Mable has not seen her grandchildren in over a year.
She
has talked to her grandchildren on the phone and through e-mails many
times. She has also seen pictures of her grandchildren. They have grown
so much since the last time they visited America.
Mable knits
scarves and blankets to send to her grandchildren in London. So far,
she has knitted two large blankets for her granddaughters. She has also
knitted a scarf for each grandchild.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Perfect Story 4.
Present
Perfect Progressive
The Present Perfect
Progressive (Continuous) is a form of the verb that shows
the action or state started in the past and continued until the present.
For example:
Lisa has been
dancing for 3 hours without stopping.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the present perfect
progressive and
how to use it.
Present
Perfect
Progressive Story 1
Who are they? What have they
been doing?
Where have they been going?
Ruth and Martha are best friends. They have been spending time
together since they were young girls. Every morning, they get dressed
and walk to the post office together. They have been walking together
to the post office every morning for the past 10 years.
Lately,
Martha has not been feeling well. Ruth has been walking to the post
office alone each morning. Then she visits Martha at home. She has been
bringing Martha her mail every morning for 2 weeks. She hopes Martha
feels better soon.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Perfect Progressive Story 1.
Present
Perfect
Progressive Story 2
Who are they? What have they
been doing?
Nick has been playing the game of marbles since he was 5 years old.
He likes to play marbles. He plays with the other kids. He also teaches
other kids how to play the game.
Lately, he has been teaching
Brian how to play marbles. He has been teaching Brian all the rules of
the game. He has been teaching Brian how to win.
Brian is Nick’s
friend. Recently, he has been learning to play marbles. He has been
wishing to play the game for many years. The past few days, his friend,
Nick, has been teaching him how to play marbles. It is a fun game.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Perfect Progressive Story 2.
Present
Perfect
Progressive Story 3
Who is he? What has he been
doing?
Jimmy sings with the boys’ choir at his church. Jimmy has a good
singing voice. He has been singing since he was very young. He has been
singing with the boys’ choir for the past 3 years. He likes to sing
with the choir.
Lately, the choir has been practicing many new
songs. They have been learning songs for their Christmas performance.
They have been practicing 2 hours every day for the last 2 weeks. They
have been working very hard.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Perfect Progressive Story 3.
Present
Perfect
Progressive Story 4
Who are they? What have they
been doing?
Marcus travels to Los Angeles a lot for work. In fact, he has been
traveling to Los Angeles once a month for over a year. Every time he
travels to Los Angeles, he stays at the same hotel. He likes the
service at this hotel. He has been staying at this hotel at least 5
days every month for over a year.
Marcus’s favorite employee
at the hotel is Benjamin. Benjamin has been working at this hotel for 2
years. He usually works as a bellhop, but lately he has been training
for a new job.
For the past 2 weeks, Benjamin has been
training to become the assistant manager of the hotel. Marcus is proud
of Benjamin because he knows Benjamin has been working hard the last 2
years.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Present Perfect Progressive Story 4.
Simple
Past
The Simple Past
is a form of the verb that shows the action or state happened in the
past.
For example:
Lisa danced
yesterday.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the simple past and how
to use it.
Simple Past Story 1
Who were they? Where did they
go? What happened?
One autumn evening, Charles and Beth went to the theater. They
attended a play. The play started at 7:00. Charles and Beth enjoyed the
theater.
After the play, Charles and Beth walked together in the
park. They walked beside the lake. The moon was bright. They talked
about their future.
When Charles and Beth went home, their
children were not asleep. They waited for Charles and Beth to return.
They were excited to hear about the theater!
Charles told the
children about the play. Then, Beth put the children to bed. Charles
and Beth were very tired. It was a good night!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Past Story 1.
Simple Past Story 2
Who is she? Where did she do?
What happened?
Last week, Beth baked a cake for Lilly’s birthday party. Lilly
wanted a strawberry cake with pink frosting. Beth was happy to bake the
cake.
First, Beth mixed the ingredients in a big bowl. Next, she
poured the cake batter into four round baking pans. She put the pans in
the oven. Finally, she baked the cakes for 20 minutes.
Then,
Beth prepared the pink frosting. After the cakes cooled, Beth stacked
them and covered them with frosting. Beth wrote Lilly’s name on top
with white frosting. She put seven candles in the cake.
On
Sunday, Beth surprised Lilly with the strawberry cake. Lilly loved her
cake! Lilly had many gifts for her birthday. But Lilly said her cake
was the best gift of them all!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Past Story 2.
Simple Past Story 3
Who were they? What did they
do? What happened?
Last night, George was at a restaurant with Clara, Charlie, and
Katherine. After dinner, George announced his engagement to Clara.
George stood next to Clara. He raised his glass. He announced the
engagement to his friends. He looked very happy!
Clara was also
at the restaurant. She sat at the table next to George. She smiled when
he announced the engagement. She showed her friends her ring. It was
very beautiful. Clara also looked very happy!
Charlie and
Katherine also sat at the table. They were excited for their friends.
Charlie congratulated George and Clara. He shook George’s hand.
Katherine looked at Clara’s ring. She hugged Clara. She was happy for
George and Clara!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Past Story 3.
Simple Past Story 4
Who were they? What did they
do? What happened?
On Saturday, the Jenson family shopped for a Christmas tree. They
got in the car. They drove to the tree farm. Mr. and Mrs. Jenson walked
around the tree farm with their kids.
The Jenson family looked
at all the trees. They looked at tall trees and short trees. They
looked at fat trees and skinny trees. They looked at every tree on the
farm. They wanted the perfect tree.
The Jenson kids finally
found the perfect tree. It wasn’t too tall or too short. It wasn’t too
fat or too skinny. The tree was exactly what they wanted. It was the
perfect Christmas tree!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Past Story 4.
Past
Progressive
The Past Progressive
(Continuous) is a form of the verb that shows the action
or state was in progress (continued) in the past.
For example:
Lisa was dancing
yesterday at 8 o’clock.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the past progressive and
how to use it.
Past
Progressive Story 1
Who was she? Where was she?
What was happening?
Yesterday, it was raining and thundering all day. Ann was playing
inside the house. She wanted to be outside. She wasn’t playing outside
because it was raining. She was feeling tired of being trapped inside
the house.
Ann was trying to keep busy inside the house. She
was reading her book until the electricity went out. Then, she decided
to practice her sewing. She was practicing sewing until lunchtime.
After lunch, she sat by the window and watched the rain.
While
Ann was watching the rain, the phone rang. Her mother was calling to
say she was coming home. She was bringing a new game. Ann and her
mother ate ice cream and played the game.
While they were playing, the rain stopped! But Ann didn’t even notice.
She was having such a good time with her mom!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Progressive Story 1.
Past
Progressive Story 2
Who were they? What were they
doing?
What was happening?
One sunny day, Billy and Timmy were delivering a box to Mr.
Thompson. The crate was full of glasses. They were carrying the box on
a cart. They were taking the glasses to Mr. Thompson’s store at the end
of the street. They were being very careful with the crate full of
glasses.
As they were passing by the school, they saw Jack and
Tom. Jack and Tom were playing soccer. Billy and Timmy asked the other
boys for help. The four boys steered the cart through the streets.
While Billy and Timmy were pulling from the front, Jack and Tom were
pushing from behind.
As they were walking, Billy and Timmy
were guiding the cart over bumps and holes. They were protecting the
glasses. When the four boys arrived at the store, Mr. Thompson was
waiting for them. While Mr. Thompson was unloading the glasses, he
thanked the boys for their hard work. None of the glasses were broken!
The boys were feeling very proud of their hard work.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Progressive Story 2.
Past
Progressive Story 3
What was he doing? What was
happening?
Last night at 7 o’clock, Nate was taking pictures of birds. He was
walking through the city park when he saw a fire. An old, empty
building near the park was on fire. Nate pulled out his camera.
He
was taking pictures of the fire when the fire trucks pulled up. The
firefighters jumped out. They hooked up their hoses. While they were
fighting the fire, Nate was taking more pictures.
The
firefighters were fighting the fire and Nate was taking pictures when
the rain started. The rain helped put the fire out. The firefighters
were clapping and Nate was cheering. The fire was finally out.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Progressive Story 3.
Past
Progressive Story 4
Who were they? What were they
doing?
What was happening?
Mitch was always driving his motorcycle too fast. Yesterday after
work, Mitch was driving his motorcycle home. While everyone else was
driving slowly, he was speeding through the streets. He wasn’t paying
attention and was driving too fast when he saw the police officer.
While
the police officer was directing traffic, he saw Mitch speeding down
the street. He was waving his arms when Mitch stopped. The police
officer wrote him a traffic ticket for speeding. Mitch was not feeling
happy when he arrived home.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Progressive Story 4.
Past
Perfect
The Past Perfect
is a form of the verb that shows the action or state was
complete before some time in the past.
For example:
Lisa had danced
before she came.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the past perfect and
how to use it.
Past
Perfect Story 1
Where were they? What
happened?
What had they done?
Last night, Dane and Emily danced in a competition. They danced a
salsa dance. They had practiced for 6 months before they danced in the
competition. They were very good.
Dane and Emily’s friends were
in the audience. Before that night, they had never seen Dane and Emily
dance. In fact, Dane and Emily had never danced in front of anyone
before the competition.
After everyone had danced, the judges
announced the winners. Dane and Emily won! They were the best dancers
in the competition. Emily said she had never practiced so hard before!
She was glad they had practiced a lot.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Perfect Story 1.
Past
Perfect Story 2
Where were they? What did
they do?
What had they done?
Last weekend, Mark and Trisha went on a date. Mark took Trisha to
the golf course. Mark loved to golf. He had learned to golf as a child.
He had even played on a team in high school.
Before that day, Trisha had never golfed. She did not know how to hold
the golf club. She did not know the rules.
Mark
taught Trisha how to play. After Trisha had learned the basics, she hit
the ball. It was a good hit! Mark had taught Trisha well.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Perfect Story 2.
Past
Perfect Story 3
Where had I gone? What had I
done?
What had I seen?
I had never seen such beautiful sights before I visited Paris in
2012. I had saved money for 5 years before I booked my trip to Paris. I
was very excited! Before my trip to Paris, I had never been out of the
United States.
When I went to Paris, I spent many days touring
the city. The city was big. Sometimes I got lost and asked for
directions. I asked for directions in French. That was easy because I
had studied French for 2 years before I visited Paris.
By the
time I left Paris, I had toured many beautiful places. The Eiffel
Tower,
Notre Dame Cathedral, and Luxembourg Gardens were just a few of the
places I saw. Before I visited Paris, I had only seen those places on
television.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Perfect Story 3.
Past
Perfect Story 4
Who had owned it? What had
they done?
The Smith family had never owned a car until they bought their
first automobile in 1906. Before they bought it, they had only used
horses and a buggy for transportation. They had never owned anything so
expensive before they bought the car.
The Smith family was very
excited about their automobile. The children had never ridden in an
automobile before their parents purchased the car. They had only seen a
few automobiles when they went to town for supplies. But nobody they
knew had ever owned an automobile before that day. They felt very lucky.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Perfect Story 4.
Past
Perfect Progressive
The Past Perfect
Progressive
(Continuous) is a form of the verb that shows the action
or state started in the past and continued until some point in the past.
For example:
Lisa had been
dancing for 2 hours before she got tired.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the past perfect
progressive and
how to use it.
Past
Perfect Progressive Story 1
Who are they? What had they
been doing?
Where had they been going?
Donald and Elizabeth had been driving to church before they
stopped. They had been driving down a dirt road when they heard a
strange noise. Donald stopped the car. He got out of the car. Then, he
helped Elizabeth out of the car. Elizabeth sat and waited for Donald.
Donald
looked at the car. It had been going for an hour or so. He knew how to
fix cars. He had been working as a mechanic for 5 years before he moved
to the country. Donald got his tools. He looked under the hood. It
seemed that the engine had been heating up. He crawled under the car.
Donald
had been working on the car for a while when Jake parked beside him.
Jake had been driving home when he saw Donald and Elizabeth on the side
of the road. Jake helped Donald fix the car. Donald thanked Jake for
his help. Elizabeth waved to Jake as they drove away. Thanks to Jake’s
help, they arrived at church on time.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Perfect Progressive Story 1.
Past
Perfect Progressive Story 2
Where were they? What had
they been doing?
Billy and the other scouts had been hiking on the mountain all
morning when they realized they were lost. They looked each direction.
They did not see the camp. They did not see the river.
The
scouts were tired because they had been hiking for four hours. They
were worried because they were lost. They sat down under a tree.
But
Billy was not worried. Billy had been hiking these mountains with his
dad his whole life. Billy’s dad had been teaching him how to use a
compass for three years. Billy climbed a tree and saw the river. He
knew the camp was north of the river. Billy looked at his compass. He
guided the scouts back to the camp.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Perfect Progressive Story 2.
Past
Perfect Progressive Story 3
Where was she? What did she
do?
What had she been doing?
Lisa slept because she had been feeling very sick. In fact, Lisa
had not been feeling well for three days. Her mother knew something was
strange because Lisa had not been acting normal. She had not been
finishing her meals for the past two days. She had not even been
playing with her friends.
The doctor visited Lisa. He had been
visiting many children since the sickness arrived. He examined Lisa. He
gave Lisa medicine. He talked to Lisa’s mother.
Lisa’s mother
had been praying for a week when Lisa woke up. Lisa looked much better.
She did not feel sick anymore. Everyone was happy that Lisa was better!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Perfect Progressive Story 3.
Past
Perfect Progressive Story 4
Where was he? What did he do?
What had he been doing?
Patrick had been playing the banjo for about 15 years. Many years
ago, his grandfather played the banjo in a band. He taught Patrick how
to play the banjo when Patrick was just 10 years old. Patrick had been
practicing the banjo ever since. He had been playing for his friends
and family for many years.
Last night, Patrick played his banjo
on a television show. He had been hoping to be on this show since he
first saw it on television 5 years ago. He played in front of a live
studio audience. The audience cheered and clapped for Patrick.
Patrick
knew he was good because he had been playing the banjo for a long time.
Now everyone knew that Patrick was a good banjo player.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Past Perfect Progressive Story 4.
Simple
Future
The Simple Future
is a form of the verb that shows the action or state will happen in the
future.
For example:
Lisa will dance
tomorrow.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the simple future and how
to use it.
Simple Future Story 1
Who is she? What will she do?
What is going to happen?
On Saturday, Katie will be one year old. Katie’s parents are going
to have a birthday party. The party is going to begin at noon on
Saturday. Many people will be at the party. Katie will have so much fun!
Katie’s
dad is going to cook hamburgers. Katie’s grandmother is going to bring
ice cream. Katie’s aunt is going to bake a cake. It will be a chocolate
cake. Katie will love her cake!
All of Katie’s relatives will
bring presents. Katie is going to open her presents after lunch. Then,
everyone will eat cake and ice cream. Katie is going to have a good
first birthday!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Future Story 1.
Simple Future Story 2
Who is she? What will she do?
What is going to happen?
This weekend, Erica is going to compete in a tennis tournament. She
will practice hard all week because she wants to win the tournament.
The winner will receive $1,000. Erica hopes she will get first place!
Erica’s
husband is going to travel to the tournament with Erica. He will watch
her compete. He will sit in the stands and cheer for Erica. He is going
to be proud of Erica even if she does not win first place.
Erica’s
parents are not going to travel to the tournament. They will watch the
tournament on television. They will cheer for Erica at home. They are
going to be proud of Erica whether she wins or loses.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Future Story 2.
Simple Future Story 3
Who is he? Where is he going?
What will happen?
Brent is an American astronaut. Today, he will travel into outer
space. At noon, his space shuttle is going to launch into space. Brent
and the other astronauts are going to travel to the International Space
Station. They will stay in space for almost 6 months.
The crew
is going to continue research at the space station. They will do some
experiments. They will record their data. They are also going to make
some repairs on the space station.
Brent will learn a lot in
space. He is going to make videos of his time on the space station. His
family will watch the videos on the internet. They will see what Brent
is doing in space.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Future Story 3.
Simple Future Story 4
What is it? What is going to
happen?
There is going to be a wedding today. At 4 o’clock this afternoon,
Megan Smith and Mark Jones are going to get married. After today, they
will be Mr. and Mrs. Mark Jones.
It is going to be a huge
celebration. Everyone will be there! They are going to serve dinner and
dessert. The best man will give a speech. Then everyone will dance. The
dance will last until midnight.
The day after the wedding, Megan
and Mark are going to leave for their honeymoon. They are going to
travel to Hawaii. They are going to stay there for 7 days. They will
have a good time in Hawaii!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Simple Future Story 4.
Future Progressive
The Future Progressive
(Continuous) is a form of the verb that shows the action
or state will be in progress at some time in the future.
For example:
Lisa will be
dancing tomorrow at 8 o’clock.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the future progressive and
how to use it.
Future
Progressive Story 1 
Who are they? What will they
be doing?
What will be happening?
Brad likes to fish. He fishes whenever he can. This weekend, he will be
fishing at the lake. It is his favorite place to fish.
Mark
is Brad’s friend. Mark likes to fish too. He also fishes whenever he
can. This weekend he will be fishing at the lake with Brad. They will
be camping at the lake all weekend.
Mark will be picking Brad
up at 8 o’clock Friday night. Brad will be ready when Mark arrives.
They
will be driving all night before they get to the lake.
They are
excited about the weekend. Brad and Mark both love to fish. They love
to fish together. They will be fishing together for many years!
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Progressive Story 1.
Future
Progressive Story 2
Who are they? What are they
going to be doing?
What will be happening?
Today, there is going to be a parade. At the beginning of the
parade, the mayor is going to be driving by in his carriage. The horse
will be pulling the carriage and the mayor will be waving to the crowd.
The crowd will be waving when the mayor passes by.
Timothy and
his grandfather will be standing in front of the store when the mayor
passes them. Timothy and his grandfather are going to be watching and
waving. Everyone is going to be having a good time at the parade.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Progressive Story 2.
Future
Progressive Story 3
Who are they? What are they
going to be doing?
What will be happening?
Sir Thomas is going to be arriving at 3 o’clock today. When Sir
Thomas arrives, the servants will be waiting. Young Charlie will also
be waiting at the door.
When Sir Thomas walks into the house,
most of the servants are going to be bowing. One servant will be
parking the car. Others are going to be preparing dinner. Charlie is
going to be carrying Sir Thomas’s suitcase into the house.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Progressive Story 3.
Future
Progressive Story 4
What is it? Where will it be
going?
What is going to be happening?
Tomorrow afternoon, the ship will be sailing to Antarctica. The
sailors are going to be working very hard when the ship sails. Some
sailors will be pulling ropes on the sails. Others are going to be
watching for icebergs. The captain is going to be navigating the ship
while it is sailing.
When the ship arrives at its destination,
some sailors are going to be resting. Others will be making repairs
to the ship. The captain is going to be exploring the land. His
assistant will be drawing a map of the land.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Progressive Story 4.
Future Perfect
The Future Perfect
is a form of the verb that shows the action or state will be complete
before some time in the future.
For example:
Lisa will have
danced by 9 o’clock.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the future perfect and
how to use it.
Future
Perfect Story 1
Who is he? What will he have
done?
What will have happened?
Mr. Jones is a farmer. He owns a big farm. He plants crops in his
fields in the spring. By the time he finishes planting this spring, he
will have planted 10 acres of crops. He is going to have planted many
crops.
Mr. Jones must finish planting before it starts to rain.
He is working hard. At this rate, he will have finished planting before
it rains. Mr. Jones and his horse will have worked many long hours by
the time they finish tonight.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Perfect Story 1.
Future
Perfect Story 2
Who are they? What will they
have done?
What is going to have happened?
Tyler and William are paddling their canoe down the river. They are
traveling a long distance through trees and canyons. They will have
paddled for many miles by the time they arrive at their destination.
They are going to have been gone for 2 weeks by the time they finish
their trip.
They are going to have seen many sights by the time
their trip is completed. They probably will have seen many wild
animals. They will have eaten many fish. They will not have seen many
other people by the end of their trip.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Perfect Story 2.
Future
Perfect Story 3
Who are they? What will they
have done?
What is going to have happened?
Brett is in the army. Tomorrow, he will leave home to join his
troops overseas for 18 months. He will have trained for 8 months by the
time he leaves. He will have worked very hard by the time he comes home.
By
the time he returns, he is going to have been gone for 18 months. His
wife will have worried about him all that time. They will have written
many letters by the time he comes home. She will be happy when
he returns safely.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Perfect Story 3.
Future
Perfect Story 4
Who are they? What will they
have done?
What is going to have happened?
John works in an automobile factory. He works on the assembly line
assembling cars. He works many hours every day. By the time he finishes
working today, he is going to have worked 10 hours. He will have
assembled over 50 cars.
Chris also works on the assembly line
in the automobile factory. In December, he will have worked there for 5
years. By the time he finishes working today, he is going to have
worked over 8 hours. He will have assembled about 40 cars today.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Perfect Story 4.
Future
Perfect Progressive
The Future Perfect
Progressive (Continuous) is a form of the verb that shows
the action or state will continue until some point in the future.
For example:
By tomorrow morning, Lisa will
have been dancing for 12 hours.
Click here
for the
full info, rules, examples and exercises on the future perfect
progressive and
how to use it.
Future
Perfect
Progressive Story 1
Who are they? What will they
have been doing?
Paul and Lindsey are going on a sleigh ride to their friend’s house
for the weekend. The snow will be deep, but their horse is very strong.
They are going to travel a long way. They will have been riding in the
sleigh for over an hour by the time they arrive.
Paul’s horse,
Midnight, will pull the sleigh over the snow. When they arrive,
Midnight will be tired because he is going to have been pulling the
sleigh for over an hour. Midnight will need food and rest because he
will have been pulling the sleigh over all that snow.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Perfect Progressive Story 1.
Future
Perfect
Progressive Story 2
Who is he? What will he
have been doing?
Pete is a window washer. Today, he is going to be washing windows
on the 13th floor of a downtown office building. He will have been
washing windows for almost 10 hours when he finishes all of the windows
on the 13th floor. He will be very tired tonight because he will have
been working so hard.
Although the work is difficult, Pete
enjoys his job. In August, he will have been working as a window washer
for 5 years. He will have been washing windows in this city for the
past 5 years.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Perfect Progressive Story 2.
Future
Perfect
Progressive Story 3
Who are they? What will they
have been doing?
Everyone is at church. They are listening to the minister. By the
time the minister finishes his sermon, the people will have been
listening to him preach for over an hour. They will have been sitting
on the hard pews for over an hour.
The minister is giving the
sermon. It is a long sermon. He will have been talking for over an hour
by the time he finishes. He will have been standing behind the pulpit
for over an hour.
Click here to download the full worksheet:
Future Perfect Progressive Story 3.
Future
Perfect
Progressive Story 4
Who is he? What will he have
been doing?
Barry is a magician. Barry has been a magician for many years. This
December, he will have been doing magic professionally for 25 years. He
will have been entertaining audiences for 25 years.
Currently, Barry is a magician in a show in Las Vegas. In October, he
is going to have been performing in Las Vegas for 3 years. He will have
been entertaining Las Vegas audiences with his card tricks for 3 years.
Click
here to download the full worksheet:
Future Perfect Progressive Story 4.
For many more
examples of the English tenses visit this section:
Examples
of English Tenses
Present Perfect for Experience
Present Perfect помогает говорить об опыте, данное время подчеркивает его приобретение в прошлом.
Этот случай применяется, когда человек рассказывает о путешествиях, какой-то уникальной или странной еде, одежде, каких-то необычных занятиях, все, что несет в себе определенный опыт.
Даже если человек пережил этот опыт десять лет назад, но эмоции еще свежи, еще хочется подчеркнуть их, вполне уместно применить Present Perfect.
Заметка:
При применении Present Perfect не следует указывать, когда произошло действие. В противном случае нужно менять грамматическое время на другое, например, Past Simple.
К примеру:
I have worn a kimono. — Present Perfect
I wore a kimono at a Japanese festival 10 years ago. — Past Simple
Один и тот же случай, однако его можно выразить двумя способами:
С эмоциями, подчеркивая действие — Present Perfect
С уточнением деталей, более информативно, но менее эмоционально — Past Simple
Данный случай применения Present Perfect исходит из логики того, что главная задача Present Perfect выразить эмоции по поводу прошедшего, а опыт — это эмоции.
Примеры Present Perfect на тему опыта
I have done a dangerous sport. — Я занимался опасным видом спорта.
I have made a meal for one hundred people. — Я готовила обед на сто человек.
I have been to Paris. — Я побывала в Париже.
I have worn a kimono. — Я носила кимоно.
I have made a speech in front of thousands of people. — Я выступал с речью перед тысячами людей.
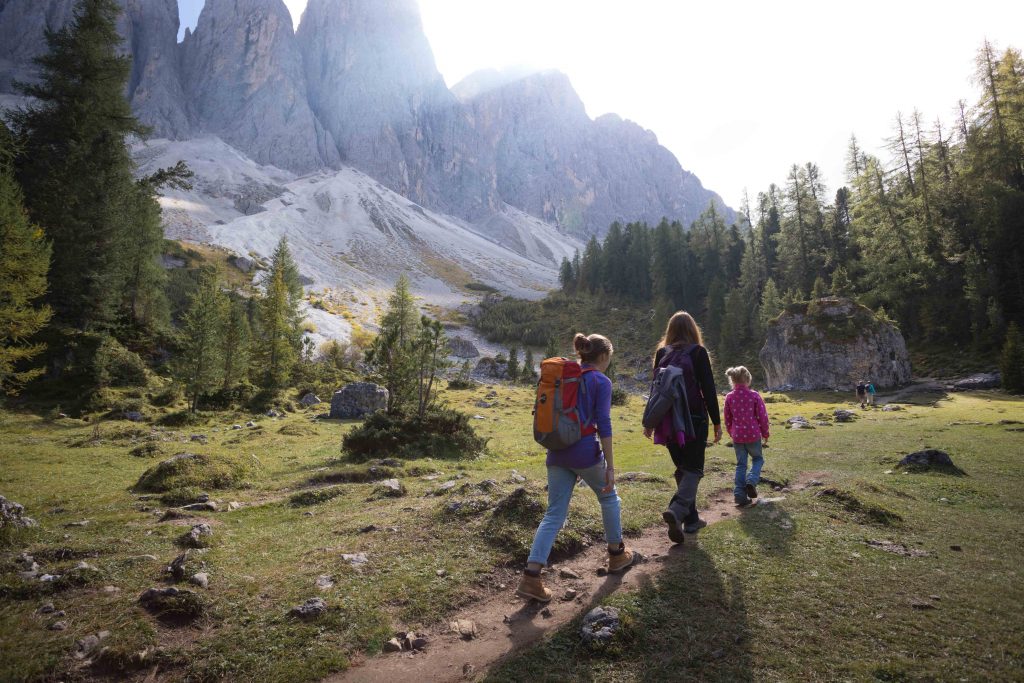




Маркеры, которые используются для указания на опыт Ever, Never
1. Ever
Чтобы спросить про опыт, очень часто используется слово Ever.
Данное наречие ставится перед смысловым глаголом.
Примеры:
Have you ever done a dangerous sport? — Вы когда-нибудь занимались опасным видом спорта?
Has she ever been to Paris? — Она когда-нибудь была в Париже?
— Вы когда-нибудь выступали перед тысячами людей?
2. Never
Чтобы указать на отсутствие опыта, используется наречие — Never
Примеры:
I have never done a dangerous sport. — Я никогда не занимался опасным видом спорта.
I have never made a meal for one hundred people. — Я никогда не готовил еду на сто человек.
I have never been to Paris. — Я никогда не был в Париже.
Been to или Been in
Примечание:
После глагола to be в форме Past Participle — been — ставится частица to, когда говорится об опыте пребывания или проживания когда-то в определенном месте.
She has been to Italy. — Она побывала в Италии.
I have been to France. — Я жила во Франции.
Но! Возможен другой вариант, когда после been ставится частица in. Этот вариант используется в двух случаях:
1. Когда Present Perfect используется для периода до данного момента.
She has been in Italy for three months. — Она находится в Италии три месяца.
2. Когда это американский английский
She has been in Italy. — Такой вариант встречается в различных пособиях американских авторов.
Уроки английского языка проводятся онлайн.
Все учебники и материалы предоставляются преподавателем.
Ответы на возможные вопросы по процессу обучения онлайн можно прочитать по ССЫЛКE
Present Perfect – настоящее совершенное время. Оно образуется с помощью глагола have/has и причастия прошедшего времени (глагол в третьей форме или с окончанием –ed).
Present Perfect используется, когда мы говорим:
о чем-то, что началось в прошлом и продолжается в настоящем:
- We have worked in this company since 2017. – Мы работаем в этой компании с 2017 года.
- They have lived here for 5 years. – Они живут здесь пять лет.
о нашем жизненном опыте к настоящему моменту:
- I have read this book. – Я прочитал эту книгу.
- He has been to India twice. – Он дважды был в Индии.
- I‘ve painted ever since I was a child. – Я рисовал с детства.
- This is the best place I have ever been to. – Это лучшее место, в котором я когда-либо был.
о чем-то, что произошло в прошлом, но имеет значение и результат в настоящем:
- I know this story. I have heard it many times. – Я знаю эту историю. Я слышал ее много раз.
- I’m not sleepy. I have slept enough. – Я не сонный. Я спал достаточно.
- Harry is not at home. He has gone to work. – Гарри не дома. Он ушел на работу.
Маркеры времени, которые используются в Present Perfect:
- never – никогда
- yet – еще
- lately – в последнее время
- since – с какого-то момента времени
- for – в течение какого-то времени
- just – только что
- already – уже
- recently – недавно
- so far – к настоящему времени, пока
- ever – когда-либо
Ниже мы рассмотрим примеры Present Perfect в разных типах предложений с переводом.
Смотрите также:
- Какие 3 формы есть у глаголов в английском языке?
- Таблица из 200 неправильных глаголов английского
- Упражнения на неправильные глаголы с ответами
Примеры утвердительных предложений
В утвердительном предложении глагол have имеет две формы – have и has. Has используется с 3-м лицом ед. числа, have – со всеми остальными.
Причастие прошедшего времени – это глагол с окончанием –ed (played, worked, danced) или глагол в третьей форме (bought, taken, put). Третью форму глагола можно найти в таблице неправильных глаголов английского языка.
Have и has в разговорной речи сокращаются: I’ve, he’s, she’s, we’ve, they’ve.
Примеры утвердительных предложений в Present Perfect
| Полная форма | Сокращенная форма | Перевод |
| He has won the competition. | He‘s won the competition. | Он выиграл соревнование. |
| They have moved to Sydney recently. | They‘ve moved to Sydney recently. | Они недавно переехали в Сидней. |
| I have already been to their concert once. | I’ve already been to their concert once. | Я уже был на их концерте один раз. |
| Kyle has made 3 mistakes in his test so far. | Kyle‘s made 3 mistakes in his test so far. | Пока что Кайл сделал 3 ошибки в тесте. |
| The writer has published a new book. | The writer‘s published a new book. | Писатель опубликовал новую книгу. |
| I have just broken the vase. | I‘ve just broken the vase. | Я только что разбил(а) вазу. |
| She has opened the window. | She‘s opened the window. | Она открыла окно. |
| We have just heard a strange noise. | We‘ve just heard a strange noise. | Мы только что услышали странный звук. |
| You have always liked flowers. | You‘ve always liked flowers. | Ты всегда любила цветы. |
| I have talked to her before. | I‘ve talked to her before. | Я разговаривал с ней раньше. |
Примеры отрицательных предложений
Отрицательная форма в Present Perfect образуется с помощью частицы not после глагола have/has и глагола с окончанием -ed или в третьей форме.
Вместо частицы not может использоваться слово never (никогда). Хотя в русском языке мы используем частицу не после никогда “я никогда не...”, в английском слова never достаточно. Например: I have not been there (Я не был там) – I have never been there (Я никогда не был там).
В разговорной речи распространена сокращенная форма: have not – haven’t, has not – hasn’t.
Примеры отрицательных предложений в Present Perfect:
| Полная форма | Сокращенная форма | Перевод |
| I have not received any letter. | I haven’t received any letter. | Я не получил накакого письма. |
| They have not been to the museum yet. | They haven’t been to the museum yet. | Они еще не были в музее. |
| We have not seen them lately. | We haven’t seen them lately. | Мы их не видели в последнее время. |
| I have not thought of it since yesterday. | I haven’t thought of it since yesterday. | Я не думал об этом со вчера. |
| My parents have not used Skype before. | My parents haven’t used Skype before. | Мои родители раньше не пользовались скайпом. |
| She has not come back from school yet. | She hasn’t come back from school yet. | Она еще не вернулась из школы.) |
| He has not lost his ticket. | He hasn’t lost his ticket. | Он не потерял свой билет. |
| The plane has not taken off yet. | The plane hasn’t taken off yet. | Самолет еще не взлетел. |
| Lola has not been there for 5 years. | Lola hasn’t been there for 5 years. | Лола не была там 5 лет. |
| Nick has not finished his exam yet. | Nick hasn’t finished his exam yet. | Ник еще не закончил свой экзамен. |
Примеры вопросительных предложений и ответов
Чтобы составить вопрос в Present Perfect, нужно have/has вынести вперед, перед подлежащим. Например:
- He has done it (Он сделал это)
- Has he done it? (Он сделал это?)
Краткий ответ состоит из Yes + местоимение, заменяющее подлежащее + have / has. No + местоимение, заменяющее подлежащее + haven’t / hasn’t. Например:
- Have they arrived? – Yes, they have. (Они приехали? – Да.)
- Has Nina called you? – No, she hasn’t. (Нина звонила тебе? – Нет.)
Специальный вопрос в Present Perfect начинается с вопросительных слов Where, What, Why, How и тд.
- Why has he done it? (Почему он это сделал?)
Примеры вопросов в Present Perfect:
| Вопрос | Перевод | Ответ | Перевод |
| Have you ever been to Paris? | Ты когда-либо был в Париже? | Yes, I have. / No, I haven’t. | Да / Нет |
| Have they invited you? | Они тебя пригласили? | Yes, they have. / No, they haven’t. | Да / Нет |
| Have you called Jane? | Ты позвонил Джейн? | Yes, I have. / No, I haven’t. | Да / Нет |
| Have we met before? | Мы раньше встречались? | Yes, we have. / No, we haven’t. | Да / Нет |
| Where have you put the bag? | Куда ты положил сумку? | On the sofa. | На диван. |
| Has she done her homework? | Она сделала домашнюю работу? | Yes, she has. / No, she hasn’t. | Да / Нет |
| Has he applied for University? | Он подал документы в университет? | Yes, he has. / No, he hasn’t. | Да / Нет |
| Has Kitty signed the contract? | Китти подписала контракт? | Yes, she has. / No, she hasn’t. | Да / Нет |
| Has the lesson started? | Урок начался? | Yes, it has. / No, it hasn’t. | Да / Нет |
| What presents has she bought? | Какие подарки она купила? | Toys and sweets. | Игрушки и сладости. |
И напоследок, чтобы закрепить материал, советую вам посмотреть видео по всем трем видам предложений в Present Perfect:
Вам может быть интересно:
- Упражнения на Present Perfect с ответами
- Тест на Present Perfect с ответами
- Примеры предложений в Past Simple
- Примеры предложений в Present Simple
Английский язык отличается разнообразием не только лексики, но и часовых форм. Отличие в том, что если в русском языке лишь три времени – прошедшее, настоящее и будущее, то английский язык богат аж 12 временных форм. Поэтому при изучении Present Perfect нужно внимательно разобрать все варианты его употребления.
Что такое Present Perfect?
Present Perfect, или как встречается в некоторых источниках Present Perfect Simple, — это настоящее совершенное время, указывающее на деяние или процесс, которые совершались в прошлом и закончилось до определенного момента в настоящем.
Большинству очень трудно понимать, ведь в русском языке всего лишь три времени – прошлое, настоящее, будущее, и никаких промежуточных вариантов быть не может. Однако английский язык придерживается иной мысли: событие может происходить в прошлом, тем не менее результат первостепенен в настоящем времени.
Например:
- I have watched a lot fo the movies with John Depp. — Я смотрел много фильмов с Джонни Деппом (фильмы были просмотрены в прошлом, при всем этом в настоящем важен результат — я имею представление, о чем идет в них речь).
- My brother has lost keys. — Мой брат потерял ключи (ключи потеряны в прошлом, но результат этого важен сейчас).
- Catherine has talked to her boyfriend over the phone. – Кэтрин поговорила по телефону со своим молодым человеком.
- Bryan has written a wonderful song. – Брайан написал чудесную песню!
Если другие перфектные времена, такие как Past Perfect Tense, Future Perfect, Past Perfect Continuous и т.д. употребляются достаточно редко, то Present Perfect просто необходимо досконально изучить, так как оно очень популярен в повседневной жизни.
Present Perfect: правила образования
Как и большинство времен английского языка образование Present Perfect происходит с помощью основного и вспомогательного глаголов.
Present Perfect образовывается с помощью вспомогательного глагола (Auxiliary verb) have, при этом основной глагол необходимо поставить в третью форму. Так, на первом месте, как и в любом утвердительном предложении английского языка стоит подлежащее, затем to have/has и глагол в третьей форме.
Subject + have/has + Verb3
Стоит также отметить, что разница в использовании между have и has зависит от подлежащего. Это две взаимозаменяемые формы.
Для 3 лица единственного числа мы используем has, во всех остальных случаях – have.
Т.е. если мы используем I/we/you/they, то вспомогательный глагол будет в форме have, если he/she/it – то has.
Например:
- I have listened to this song before. – Я слышал эту песню ранее.
- She has started worked hard lately. – В последнее время она начала очень много работать.
- We have been very tired at the time of travel. – Мы очень сильно устали вовремя путешествия.
- He has already seen his new boss. – Он уже виделся со своим новым начальником.
- Samantha has entered the university. – Саманта поступила в университет.
- The dog has stolen her ball inadvertently. – Собака нечаянно украла её мячик.
Что касается третьей формы основного глагола, то она может образовываться двумя способами. Большая часть из них является неправильными и форму Participle II нужно смотреть в таблице неправильных глаголов. Если же основного глагола там нет, значит он является правильным, и для образования третьей формы нужно просто добавить окончание –ed.
Например, неправильные глаголы:
- to lose – lost – lost;
- to bring – brought – brought;
- to catch – caught – caught;
- to buy – bought – bought;
- to send – sent – sent.
Правильные глаголы:
- to work – worked – worked;
- to listen – listened – listened;
- to paint – painted – painted;
- to receive – received – received;
- to enter – entered – entered.
Например:
| Peter has lost control of the car. | Питер потерял контроль над управлением автомобиля. |
| My grandfather has been very sick. | Мой дедушка очень сильно заболел. |
| The husband has bought Elizabeth a new phone. | Муж купил Элизабет новый телефон. |
| Bogdan has worked at this plant since January. | Богдан работает на этом заводе с января. |
| Kate has lost the keys. | Кейт потеряла ключи. |
| I have visited three stores today. | Я сегодня посетила три магазина. |
| Megan has painted a landscape today. | Мэган сегодня нарисовала пейзаж. |
| He has gone to the cinema with Ann. | Он пошел в кинотеатр с Аней. |
| We have already left the hotel. | Мы уже покинули гостиницу. |
Каждое время характеризуется особыми наречиями, которые и помогают определить какое именно время использовано в предложении.
Для Present Perfect характерны такие слова, как already (уже), yet (уже/еще не) – используется только в конце предложения, ever (когда-либо), never (никогда) и т.д.
Например:
| My brother has just eaten. | Мой брат только что поел. |
| Peter has not come from London yet. | Питер еще не приехал из Лондона. |
| My sister has just joined to the dance club. | Моя сестра недавно присоединилась к танцевальному кружку. |
| Christina has already left. | Кристина уже уехала. |
| My mom has never tasted pineapple. | Моя мама никогда не пробовала ананас. |
| I have learned Italian since the fifth grade. | Я учу итальянский язык с пятого класса. |
| My family has not been in their hometown for ten years. | Моя семья не была в своем родном городе уже десять лет. |
| Jim has not already taken out the rubbish from the kitchen. | Джим до сих пор не вынес мусор с кухни. |
| Christopher has never been in Scotland before. | Кристофер никогда не был в Шотландии прежде. |
| I have read many books lately. | За последнее время я прочитала множество книг. |
ARVE Error: Mode: lazyload not available (ARVE Pro not active?), switching to normal mode
Present Perfect: формы предложения
Как и в любом другом времени в Present Perfect можно использовать три типа предложений – утвердительные (Affirmative), отрицательные (Negative) и вопросительные (Interrogative).
Утвердительные предложения Present Perfect
В утвердительных предложениях прямой порядок слов: всегда на первом месте стоит подлежащее (лицо или предмет, выполняющее действие), затем идет сказуемое, которое выражено вспомогательным глаголом have или has и основным глаголом в третьей форме.
Subject + have / has + Past Participle
Примеры:
| He has never been to Spain. | Он никогда не был в Испании. |
| Jack has already played football today. | Джек сегодня уже играл в футбол. |
| The commission has already published the results of the exam. | Комиссия уже опубликовала результаты экзамена. |
| I have never done such things before. | Я до этого никогда не делал такие вещи. |
| Mary has studied English since 2004. | Мэри изучает английский язык c 2004. |
| I have just finished reading the book. | Я только что закончила читать книгу. |
| Up to now we have walked four kilometers. | К этому времени мы прошли четыре километра. |
| Maxim has already known us for a long time. | Максим знал нас уже долгое время. |
| The regional construction company has built this penthouse. | Пентхаус был построен региональной строительной компанией. |
| Bella has already written the letter to her brother. | Белла уже написала письмо своему брату. |
При образовании пассивного залога после вспомогательного глагола have появляется глагол to be в третьей форме, а затем уже идет основной глагол в Past Participle. Связано это с тем, что в таких предложениях подлежащее не выполняет действие, а, наоборот, — действие происходит над ним.
Subject + have / has + been + Verb 3
Например:
| The lesson has been held excellent in the first class. | Урок был проведен в первом классе на отлично. |
| The apartment has been shown to us by a realtor. | Квартира была показана нам риелтором. |
| We have been introduced to a new teacher of a foreign language. | Нам был представлен новый учитель иностранного языка. |
| She has been transferred to another ward. | Её перевели в другую палату. |
| Oatmeal porridge has been given to us this morning. | Нам подали овсяную кашу сегодня на утро. |
| The house has been built. | Дом был построен. |
| They have been examined in the morning today. | Они были проэкзаменованы сегодня утром. |
| The window has been broken by Sebastian. | Окно разбито Себастьяном. |
| His bicycle has been stolen three days ago. | Его велосипед украли три дня назад. |
Не стоит также забывать, что вспомогательный глагол может сокращаться для упрощения речи, например:
| Употребление полной формы | Употребление сокращенной формы |
| You have shown the room. | You’ve shown the room. |
| I have worked. | I’ve worked. |
| My friend has come. | My friend’s come. |
| You have changed. | You’ve changed. |
| Ross has bought the car. | Ross’s bought the car. |
| Monica has understood a new topic. | Monica’s understood a new topic. |
Очень часто при использовании сокращенной формы в утвердительной форме предложения Present Perfect можно перепутать с Present Simple. Однако отличить Present Perfect и Present Simple можно благодаря смысловому глаголу в третьей форме в Past Participle.
Например:
| Present Simple | Present Perfect |
| Elizabeth’s the best pupil in the form. — Элизабет – лучшая ученица в классе. | Elizabeth’s forgotten the copybook in the classroom. — Элизабет забыла тетрадь в классе. |
| Mike’s a teacher at the university.- Майк – преподаватель в университете. | Mike’s taught at the university since 2017. — Майк преподает в университете с 2017 года. |
| Amanda’s a waiter at a roadside cafe. — Аманда – официант в придорожном кафе. | Amanda’s worked as a waiter at a roadside cafe for eight years. — Аманда работает официантом в придорожном кафе восьмой год. |
| Christina’s a little girl. — Кристина – маленькая девочка. | Christina’s broken a cup. — Кристина разбила чашку. |
| She’s Englishwoman. — Она – англичанка. | She’s lived in England since last year. — Она живет в Англии с прошлого года. |
Отрицательные предложения Present Perfect
Отрицательные предложения в Present Perfect образуются по такому же принципу, как и утвердительные. Единственное отличие в том, что между вспомогательным и основным глаголом появляется отрицательная частица not.
Subject + have / has + not + Past Participle
Например:
| Mary has not learnt Italian before. | Мэри не учила итальянский язык раньше. |
| My husband has not been to America. | Мой муж никогда не был в Америке. |
| This pupil has not done his task. | Этот ученик не выполнил задание. |
| Kate has not heard that fairytale before. | Кейт не слышала эту сказку раньше. |
| My brother has not come back home yet. | Мой брат пока что не вернулся домой. |
| Her husband has not been an angry man. | Её муж не был злым человеком. |
| James has not done his homework yet. | Джеймс еще не сделал домашнее задание. |
| She has not forgotten. | Она не забыла. |
Стоит также помнить, что вспомогательный глагол и отрицательная частица могут сокращаться и иметь следующие формы:
- have + not = haven’t;
- has + not = hasn’t.
Например:
| Употребление полной формы | Употребление сокращенной формы |
| I have not seen you for ages. | I haven’t seen you for ages. |
| Rachel has not heard me. | Rachel hasn’t heard me. |
| Catherine has not wanted to see us. | Catherine hasn’t wanted to see us. |
| Mary has not switched off the light. | Mary hasn’t switched off the light. |
| They have not opened books. | They haven’t opened books. |
| You have not finished it today. | You haven’t finished it today. |
Вопросительные предложения Present Perfect
В вопросительном предложении на первое место всегда выносится вспомогательный глагол have или has, затем идет подлежащее и потом основной глагол в Past Participle. При этом вспомогательный глагол отдельно не переводится.
Have / has + subject + Past Participle
Например:
| Has Linda succeeded to pass the exam? | Удалось ли Линде сдать экзамен? |
| Has Amanda written this novel? | Аманда написала этот роман? |
| Have you ever been to Paris? | Ты когда-нибудь в Париже? |
| Has John listened to this song? | Слышал ли Джон эту песню? |
| Have your mother already met your boyfriend before? | Твоя мам когда-нибудь встречалась с твоим парнем ранее? |
| Has teacher come yet? | Учитель уже пришел? |
Такая схема подходит только для альтернативных и общих вопросов. Остальные типы вопросов строятся по другой схеме.
При построении специального типа вопроса на первом месте стоит вопросительное слово, а затем уже такой же порядок слов, как и при общем типе.
Interrogative word + have / has + subject + Past Participle
Например:
| How have they moved to Germany? | Как они переехали в Германию? |
| For how much has Joey bought this jacket? | За сколько Джои купил этот пиджак? |
| When have they invented this theory? | Когда они изобрели эту теорию? |
| What has mother made for breakfast? | Что мама приготовила на завтрак? |
| When has she invited them to the party? | Когда она пригласила их на вечеринку? |
| Why have they not finished the bridge? | Почему они не достроили мост? |
Четвертый тип вопроса – разделительный. При построении такого типа вопроса сохраняется порядок слов как в утверждении или отрицании, а после них добавляется вопросы в короткой форме.
Например:
| The builders have not completed the new house, have they? | Строители не достроили новый дом, не так ли? |
| Our football team has played today’s match, has not it? | Наша футбольная команда сыграла сегодня матч, не так ли? |
| The secretary has lost important papers under the new contract, has not she? | Секретарь потеряла важные бумаги по новому контракту, не так ли? |
| Our family has left America, has not it? | Наша семья уехала из Америки, не так ли? |
| You have already had dinner, have not you? | Ты уже пообедал, не так ли? |
| You have never been to Australia, have you? | Ты никогда не был в Австралии, не так ли? |
| She has never read a book more interesting than this, has she? | Она никогда не читала книгу интереснее, чем эта, не так ли? |
Что касается ответов, то в специальных и альтернативных вопросах в Present Perfect необходимо формулировать полное предложение. В остальных случаях можно обойтись кратким ответом на вопрос.
Например:
- Has Charlie turned off the lamp? – Yes, she has./No, she hasn’t.
Чарли выключила лампу? – Да./Нет. - Has Cristina studied German or Italian? – Cristina has studied German.
Кристина изучает немецкий или итальянский язык? – Она изучает немецкий язык. - Your elder sister has given birth to a child, has not she? – No, she has not.
Твоя старшая сестра родила ребенка, не так ли? – Нет.
Если Вы устали учить английский годами?
Наши читатели рекомендуют попробовать 5 бесплатных уроков курса «АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ДО АВТОМАТИЗМА» с Анастасией Божок.
Те, кто посещают даже 1 урок узнают больше, чем за несколько лет!
Удивлены?
Получите 5 бесплатных уроков здесь…
Без домашки. Без зубрежек. Без учебников
Из курса «АНГЛИЙСКИЙ ДО АВТОМАТИЗМА» Вы:
- Научитесь составлять грамотные предложения на английском без заучивания грамматики
- Узнаете секрет прогрессивного подхода, благодаря которому Вы можете сократить освоение английского с 3 лет до 15 недель
- Будете проверять свои ответы мгновенно + получите доскональный разбор каждого задания
- Скачаете словарик в форматах PDF и MP3, обучающие таблицы и аудиозапись всех фраз
Получить 5 уроков бесплатно можно тут
Present Perfect: употребление
Present Perfect используется в тех случаях, когда мы говорим про действие, которое совершилось в прошлом, но результат которого важен в настоящем.
Например:
- I know Peter. I have already met him. – Я знаю Питера. Я уже видел его.
- I have closed the house. – Я замкнула дом. (Двери дома закрыты).
Рассмотрим еще несколько случаев, в которых мы используем Present Perfect.
ARVE Error: Mode: lazyload not available (ARVE Pro not active?), switching to normal mode
Акцентирование внимания на результате действия
В английском языке используется Present Perfect, когда необходимо обратить внимание не на само действие в прошлом, а на его результат. Продолжительность процесса не имеет в данном случае значения.
Пример:
| I have just eaten, so I do not want a cake. | Я только что покушал, поэтому я не хочу пирожное. (Действие произошло, ужин съеден, и как результат – нет чувства голода). |
| Mike has lost his passport. | Майк потерял паспорт. (Результат налицо – паспорта у Майка нет). |
| The teacher has had a wonderful lesson. | Учитель провел замечательный урок. (Урок уже прошел, его оценили на должном уровне). |
| My friend has found a wonderful book. | Мой друг нашел замечательную книгу. (Книга уже находится у друга). |
| My dog has tore up my notebook with my homework. | Моя собака разорвала мою тетрадь с домашним заданием. (Неважно когда это произошло, мы наблюдаем результат – остатки от тетради). |
| I have prepared a dinner for my family. | Я приготовил праздничный ужин для своей семьи. (Результат виден – приготовленные блюда для ужина). |
| Mrs. Brown has gone to the theatre. | Миссис Браун пошла в театр. (Как результат – её нет дома). |
К данному случаю употребления можно также отнести те ситуации, когда прошедшее действие является причиной совершенного действия в настоящем времени.
Например:
- Edward can not get into the house. He has lost the keys. – Эдвард не может попасть в дом. Он потерял ключи. (В данный момент Эдвард не может оказаться в доме, потому что в прошлом – день или неделю назад – он где-то оставил свои ключи).
- Richard can not go to the United Kingdom. He has not made a foreign passport. – Ричард не может поехать в Великобританию. Он не сделал загранпаспорт. (Сейчас в настоящее время Ричард не может посетить страну, потому что в прошлом он не сделал документы).
С перфектными наречиями
Present Perfect может использоваться в сложных предложениях, для того, чтобы указать на действие которое закончилось недавно.
Например:
| At the moment I have read nine books. | На данный момент я прочитала девять книг. |
| Mom has just made soup. | Мама только что приготовила суп. |
| I still have not seen this movie. | Я до сих пор не видела это фильм. |
| The police have not found the thieves yet who robbed our house. | Полиция до сих пор не нашла воров, которые ограбили наш дом. |
| Kate has recently got the rights. | Недавно Кейт получила права. |
| I have already written the essay for the next lesson. | Я уже написала сочинение на следующий урок. |
Среди таких перфектных наречий есть те, которые используются между вспомогательным и основным глаголами (already, just, ever, never), и те, которые стоят в начала либо конце предложения (yet, up to now, recently).
Например:
- Up to now Kate has not found her glasses. – Кейт до сих пор не нашла свои очки.
- You haven’t shown me your dairy book yet. – Ты еще не показала мне свой дневник.
- I have already told to children a fairytale. – Я уже рассказала детям сказку.
Отдельного внимания заслуживает указатель времени Present Perfect yet. Зачастую оно используется в отрицательных и вопросительных предложениях и стоит в конце. Ответ тоже можно давать краткий.
Например:
- Has Jim finished the article yet? – Not yet.
Джим уже закончил статью? – Ещё нет. - Have you learned to ride a bicycle yet? – Not yet.
Ты уже научился кататься на велосипеде? – Еще нет.
Наречие before также используется только в предложениях вопросительных (interrogative) и отрицательных (negative).
Например:
- Have you heard this song before? – Слышал ли ты эту песню ранее?
- Have you seen Thomas before? – Виделась ли ты с Томасом ранее?
Рассказ о своем опыте
Используется Present Perfect также для того, чтобы акцентировать внимание непосредственно на действие, а не на время его совершения.
Например:
| My brother has listened to the new album of this group. | Мой брат слушал новый альбом этой группы. |
| I have already gone to this city. | Я уже ездила в этот город. |
| Christina has passed this poem. | Кристина сдавала это стихотворение. |
| My family has already traveled to America. | Моя семья уже путешествовала в Америку. |
| My friends and I have already watched this movie five times. | Мы с друзьями смотрели этот фильм уже пять раз. |
| She has looked through the book twice. | Она просмотрела всю книгу уже дважды. |
В таких предложениях нередко можно встретить числительные.
Например:
- Our family has already visited this picture gallery four times. – Наша семья посещала эту картинную галерею уже четыре раза.
- Christopher has already traveled abroad twice. – Кристофер путешествовал за границу уже дважды.
- Jennifer has gone to the competition for the third time. – Дженнифер ездила на соревнования уже в третий раз.
В данных предложениях стоит внимательно отнестись к словосочетанию «быть где-то». Так, конструкция have been to означает непосредственно поездку, но из которой человек уже вернулся обратно.
Например:
- Matt has been to Poland only once. – Мэтт был в Польше всего один раз.
Конструкция have been in означает, что человек еще не вернулся из указанного места, например:
- Family of Browns has been in New York for five years. – Семья Браунов в Нью-Йорке уже пять лет.
Словосочетание have gone to в отличие от двух предыдущих конструкций означает, что человек, о котором идет речь, только отправился куда-то, например:
- Peter can’t buy the book, because the owner has already gone home. – Питер не купил книгу, потому что владелец ушел уже домой.
Чтобы выделить, сколько раз произошло действие
Present Perfect используется для того, чтобы обратить внимание на то, сколько раз именно совершалось действие, а не где и когда.
Примеры:
| I have rewatched the film for the third time. | Я пересмотрела фильм уже третий раз. |
| We have travelled abroad for the first time. | Мы путешествуем за границу впервые. |
| It is the second time when Jim has moved to another city. | Джим переезжает в другой город уже во второй раз. |
| Marina has gone to the international competition for the fifth time. | Марина ездила на международный конкурс в пятый раз. |
| For the first time I have gone to the opera house. | Впервые я ходила в оперный театр. |
| My friend has written the poem himself a third time. | Мой друг сам написал стихотворение в третий раз. |
Если период, в который случилось действие, еще не закончился
Примеры:
| She has returned to London this week. | Она вернулась в Лондон на этой неделе. |
| I have finished writing this evening. | Я закончила писать произведение сегодня вечером. |
| My mother has baked a cake in the morning. | Моя мама испекла торт утром. |
| Our group has rehearsed this week. | Наша группа репетировала на этой неделе. |
| Lessie has called three times this morning. | Лесси звонила трижды сегодня утром. |
Present Perfect в роли Present Perfect Continuous
В данном случае Present Perfect используется для того, чтобы действие продолжается до момента совершения разговора. В такой ситуации используется Present Perfect в тех случаях, когда используются глаголы, которые указывают на продолжительность или указывают на состояние.
Примеры:
| She has already bought herself a new jacket. | Она уже купила себе новую куртку. |
| Frank has worked for eight hours. | Фрэнк работает уже в течение восьми часов. |
| Don has taught French for four years. | Дон учит французский уже четыре года. |
| My mother has forgotten to give her a book to her grandmother. | Моя мама забыла отдать бабушке книгу. |
| I have realized what this movie is about. | Я поняла, о чем этот фильм. |
| I have finally realized what he said. | Я наконец-то осознала его слова. |
Одной небольшой хитростью для того, чтобы понять, что это именно Present Perfect, а не Present Perfect Continuous, является наличие в предложении предлога «for ages».
Например:
- Joseph has known Marina for ages. – Джозеф знает Марину целую вечность.
- I have not got enough sleep for ages. – Я нормально не высыпалась уже очень давно.
ARVE Error: Mode: lazyload not available (ARVE Pro not active?), switching to normal mode
Present Perfect с предлогами since и ever since
Present Perfect используется в сложноподчиненных предложениях времени. Предлоги since и ever since считаются также маркерами данного времени.
Например:
| Chris has been with the firm since he moved to London. | Крис работает в этой фирме с тех пор, как он переехал в Лондон. |
| My dad has gone to play football since he met Jim. | Мой папа ходит играть в футбол с тех пор, как он познакомился с Джимом. |
| I’ve danced ever since I saw Archie’s performance on TV. | Я занимаюсь танцами с тех пор, как увидела выступление Арчи по телевизору. |
| I have learned English since I started studying at school. | Я учу английский язык с тех пор, как начала учиться в школе. |
| Evelyn has not often drawn since she found herself some extra work. | Эвелин нечасто рисует с тех пор, как нашла себе дополнительную работу. |
| Frank has not been on social networks since he started playing tennis. | Фрэнк не сидит в социальных сетях с тех пор, как начал заниматься теннисом. |
Present Perfect Tense с придаточными времени
Present Perfect используется в сложноподчиненных предложениях. При этом главное предложение образуются при помощи Future Simple, а придаточное – при помощи Present Perfect. Соединительными предлогами выступают as soon as, after, before и т.д.
Как правило, такие предложения используют для того, чтобы акцентировать внимание на том, что одно действие произойдет лишь тогда, когда будет исполнено второе.
Примеры:
| John will call me as soon as he has got home. | Джон позвонит мне, как только доберется домой. |
| While Clark has not begun to learn new words, he will not get a high rating. | Пока Кларк не начнет учит новые слова, он не получит высокую оценку. |
| We’ll see each other after Mike has visited his grandmother. | Мы увидимся после того, как Майк съездит к бабушке. |
| Before my family has gone on a trip, I’ll finish the book. | До того как наша семья поедет в путешествие, я допишу книгу. |
| Michael will go on a picnic after he has done his homework. | Майкл пойдет на пикник после того, как сделает домашнее задание. |
| I’ll take up the new order after I have got paid for my past work. | Я возьмусь за новый заказ после того, как получу деньги за свою прошлую работу. |
Чтобы рассказать недавнюю новость
Основное предложение образуется при помощи Present Perfect, а остальные, в которых раскрываются подробности новости – в Past Simple или Past Continuous.
Примеры:
| John has finished his studies. He received a diploma and found a job. | Джон закончил обучение. Он получил диплом и нашел работу. |
| I have won an international grant. Next I will develop the project. | Я выиграла международный грант. Дальше я буду заниматься разработкой проекта. |
| My mother has left for the capital. She wanted to get the job of her dreams. | Мама уехала в столицу. Она сказала, чтобы устроиться там на работу ее мечты. |
| The famous writer has finished his literary work. He said that he would change his occupation. | Знаменитый писатель закончил свою литературную деятельность. Он заявил, что сменит род занятий. |
| David has received the award. He witnessed a robbery and detained a thief. | Дэвид получил награду. Он стал свидетелем ограбления и задержал вора. |
| My friend has divorced her husband. She found out that he deceived her and said that she wanted to start a new life. | Моя подруга развелась с мужем. Она узнала, что он ей изменят и сказала, что хочет начать новую жизнь. |
Present Perfect и Past Simple
Очень часто при переводе многие путают, когда уместно использование Present Perfect, а когда Past Simple. Present Perfect используется для того, чтобы описать действие, которое еще ни разу не делалось, а Past Simple – когда делалось ранее.
Сравнение двух времен в таблице:
| Present Perfect | Past Simple |
| I have not been to Vegas. – Я не была в Вегасе.
(Никогда ранее в жизни). |
I did not go to Vegas last month. – Я не была в Вегасе в прошлом месяце.
(В прошлом месяце или году, но когда-то ранее была). |
| Susan have smoked cigarette. – Сюзанна курила сигареты.
(Когда-то ранее, может быть, пробовала). |
Susan smoked cigarette. – Сюзанна курила сигареты.
(В какой-то конкретный день). |
| My father have prepared dinner. – Мой отец приготовил обед.
(Когда-то ранее, в какой-то день семейной жизни). |
My father prepared dinner. – Мой отец приготовил обед.
(Либо вчера, на прошлой неделе, конкретно в какой-то день). |
| Lukas have not jumped with parachute. – Лукас не прыгал с парашютом.
(Никогда ранее в жизни). |
Lukas did not jump with parachute. – Лукас не прыгал с парашютом.
(Вчера, несколько дней назад, однако, когда-то пробовал). |
Упражнения
Упражнение можно скачать тут.
Заключение
Несмотря на то что случаев употребления Present Perfect довольно-таки много, при постоянной практике грамматика данного времени не будет казаться настолько сложной, как на первый взгляд. Главное – немного усердия и от сомнений не останется и следа!
Понятие настоящего времени в английском языке не всегда совпадает с нашим. Одним из самых ярких примеров такого различия как раз является Present Perfect.
В этой статье мы разберемся, что такое Present Perfect, как оно образуется, в каких случаях употребляется, каким правилам подчиняется и закрепим знания на реальных примерах предложений с переводом.
Что такое Present Perfect Tense?
Present Perfect Tense (Present Perfect) — это настоящее совершенное время в английском языке. Оно обозначает действие, которое завершилось в настоящий момент времени.
В этом и состоит основная сложность времени Present Perfect для изучающих. В русском языке нет времени аналогичного Present Perfect. Для нас если что-то происходит сейчас — это и есть настоящее, а если совершилось — это уже прошлое.
Но не для англичан. Они воспринимают время немного по-другому. По логике носителей языка, действие вполне может закончиться и в настоящем или близко к настоящему моменту. Для выражения такой связи прошлого с настоящим и существует Present Perfect.
Из-за этих особенностей в понимании действий и времени — на русский язык Present Perfect обычно переводится глаголом в прошедшем времени.
I have already done my homework — Я уже сделал домашнее задание
В этом примере используется время Present Perfect (have done), потому что речь идет о том, что действие (работа над домашним заданием) закончилось совсем недавно.
Но на русский язык мы переводим предложение используя прошедшее время (уже сделал).
Как образуется Present Perfect?
Время Present Perfect образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола have / has и Past Participle (третьей формы смыслового глагола: V3).
Вспомогательный глагол меняется в зависимости от подлежащего:
- I / You / We / They → have (для 1-го, 2-го лица и форм множественного числа)
- She / He / It → has (для 3-го лица единственного числа)
Завершает конструкцию времени Present Perfect смысловой глагол в третьей форме (V3).
Если смысловой глагол правильной формы — то его третья форма (V3) образуется при помощи окончания -ed.
Если смысловой глагол неправильный — то его третью форму (V3) берем из таблицы неправильных глаголов.
Например:
- to try → tried (пытаться)
to cook → cooked (готовить)
to finish → finished (заканчивать) - to get → got (получать)
to keep → kept (хранить)
to see → seen (видеть)
Утверждение:
Утвердительное предложение в Present Perfect образуется при помощи вспомогательного глагола have / has и смыслового глагола с окончанием -ed для правильных глаголов или третьей формы неправильного глагола (V3) по формуле:
- I / You / We / They + have + Ved (V3)
- She / He / It + has + Ved (V3)
I have decided — Я решил
You have played — Ты играл
He has done — Он сделал
It has turned on — Оно включилось
В предложениях и повседневной речи часто можно встретить сокращенную форму вспомогательных глаголов have / has. Она образуется при помощи добавления к подлежащему ‘ve (для have) или ‘s (для has):
- I have = I’ve
- You have = You’ve
- We have = We’ve
- They have = They’ve
- She has = She’s
- He has = He’s
- It has = It’s
I’ve done my tasks — Я выполнил свои задачи
He’s washed the dishes — Он вымыл посуду
Отрицание:
Отрицательные предложения в Present Perfect образуется при помощи добавления частицы not после вспомогательного глагола have / has, но перед основным смысловым глаголом. Формула выглядит следующим образом:
- I / You / We / They + have not + Ved (V3)
- She / He / It + has not + Ved (V3)
I have not done my homework — Я не сделал домашнюю работу
They have not come — Они не пришли
She has not finished her tasks — Она не выполнила свои задачи
It has not turned on — Оно не включилось
В отрицании частицу not можно сократить путем присоединения ее к вспомогательному глаголу have / has:
- Have not = haven’t
- Has not = hasn’t
I haven’t washed my hair — Я не помыл волосы
She hasn’t been to London yet — Она еще не была в Лондоне
Вопрос:
Вопросительное предложение в Present Perfect образуется путем постановки вспомогательного глагола have / has в начало предложения. Формула будет такой:
- Have + I / You / We / They + Ved (V3)
- Has + She / He / It + Ved (V3)
Have I bought all the presents? — Я купил все подарки?
Have you finished the classes? — Ты закончил занятия?
Has she just arrived home? — Она только что приехала домой?
Has it turned on? — Оно включилось?
Специальные вопросы образуются при помощи question words (вопросительных слов). Таких, как when (когда), how (как), what (что), where (где) и других. Далее идет такой же порядок слов, как и в вопросе.
- QW + have + I / You / We / They + Ved (V3)
- QW + has + She / He / It + Ved (V3)
What has he just said? — Что он только что сказал?
How long have you knocked on the door? — Как давно ты стучал в дверь?
Когда употребляется Present Perfect?
А сейчас рассмотрим самые распространенные случаи употребления и использования времени Present Perfect в речи:
- Завершенное действие в настоящем
В таком случае акцент ставится на результат завершенного действия. Другими словами, когда результат действия виден в настоящем.
I have cooked a good dinner — Я приготовил хороший ужин (действие завершилось, результат — хороший ужин)
I know Nina. We have already met — Я знаю Нину. Мы уже встречались (встреча произошла в прошлом, но нас интересует результат в настоящем)
- Незавершенное действие в настоящем
Время Present Perfect используется в случае, когда мы описываем действие, которое началось в прошлом, еще не закончилось в настоящем, но результат очевиден.
I’ve written five pages of the new book this morning — Я написал пять страниц новой книги этим утром (утро еще не закончилось, он может написать еще несколько страниц)
She has finished watching “Harry Potter” this week — Она закончила смотреть «Гарри Поттера» на этой неделе (неделя еще идет, но она уже закончила смотреть фильм)
- Факт действия / личный опыт
Если говорящему важно подчеркнуть факт какого-то свершившегося события без точного указания времени — на помощь также приходит Present Perfect. Часто это время используется, когда мы говорим о своем прошлом опыте или же, спрашиваем об этом своего собеседника.
I have been to Bratislava — Я был (бывал) в Братиславе
В вопросе, когда мы интересуемся фактом из чьей-то жизни — используем также Present Perfect:
Have you ever been to France? — Ты когда-нибудь был (бывал) во Франции?
Маркеры времени Present Perfect
Present Perfect употребляется с неточными выражениями и словами, которые указывают на еще не закончившийся период времени
- never (никогда)
- ever (когда-либо)
- already (уже)
- yet (еще) / not yet (еще нет)
- often (часто)
- lately (в последнее время)
- just (только что)
- once (однажды)
- recently (недавно)
- before (раньше)
- today (сегодня)
- this week (на этой неделе)
- this year (в этом году)
- for an hour (в течение часа)
- for a long time (долгое время)
- since two o’clock – с двух часов
- ince December – с Декабря
Примеры предложений Present Perfect с переводом
Утвердительные:
I’ve studied English since my childhood — Я учил английский язык с детства
She has visited this beauty shop recently — Она недавно заходила в этот магазин косметики
People have walked on the Moon — Люди ходили по Луне.
We’ve just eaten, so we don’t want to go to the cafe — Мы только что поели, так что не хотим идти в кафе
I have just cut my finger — Я только что порезал свой палец
Отрицательные:
He has not returned from school yet — Он еще не вернулся из школы
I haven’t bought the new car. This is my old one — Я не купил новую машину. Это старая
Jane hasn’t been to Asia yet — Джейн еще не была в Азии
I have not been at university this week because of the flu — Я не был на этой неделе в университете из-за гриппа
I haven’t replaced the batteries in the doorbell — Я не заменил батарейки в дверном звонке
Вопросительные:
Have you seen this film about space? — Ты видел этот фильм о космосе?
Has Jimmy bought the tickets yet? — Джимми уже купил билеты?
How many deals has she made at the moment? — Сколько сделок она заключила на текущий момент?
How much coffee have you drunk today? — Сколько кофе ты сегодня выпил?
How long have you known Mary? — Как давно ты знаешь Мэри?