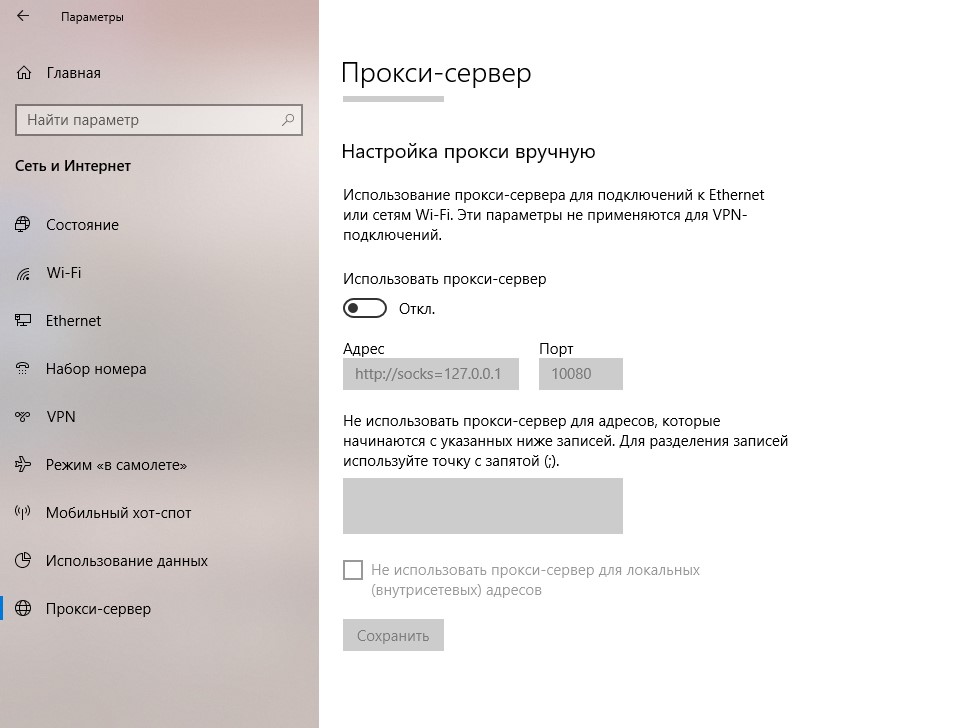
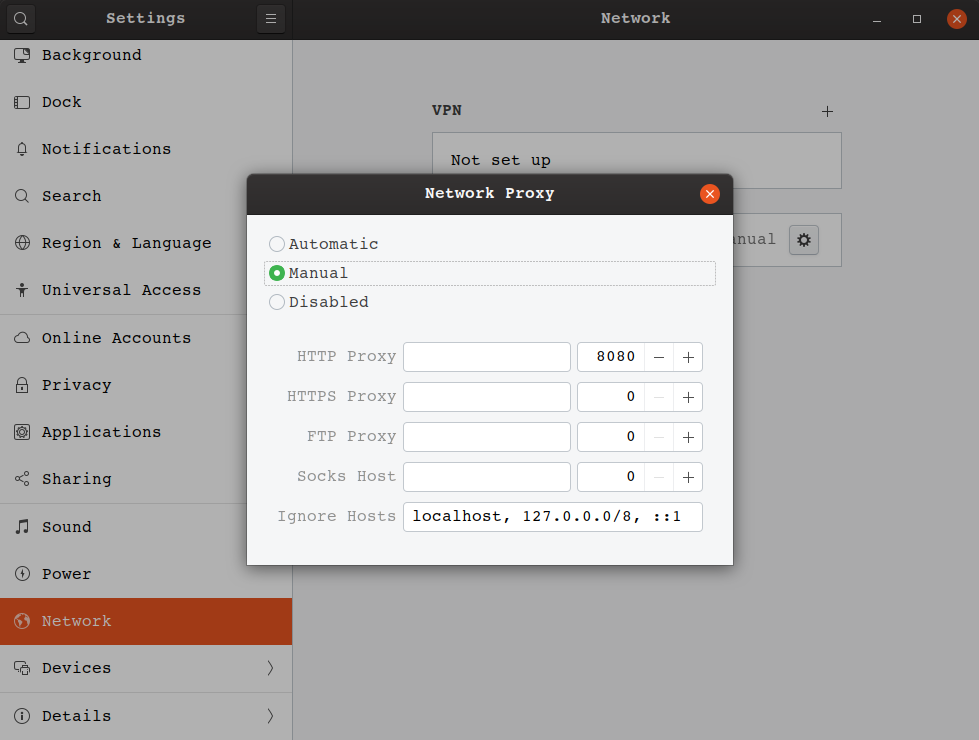
For Wikipedia’s policy on editing from open proxies, please see Wikipedia:Open proxies. For other uses, see Proxy.
Communication between two computers connected through a third computer acting as a proxy server. This can protect Alice’s privacy, as Bob only knows about the proxy and cannot identify or contact Alice directly.
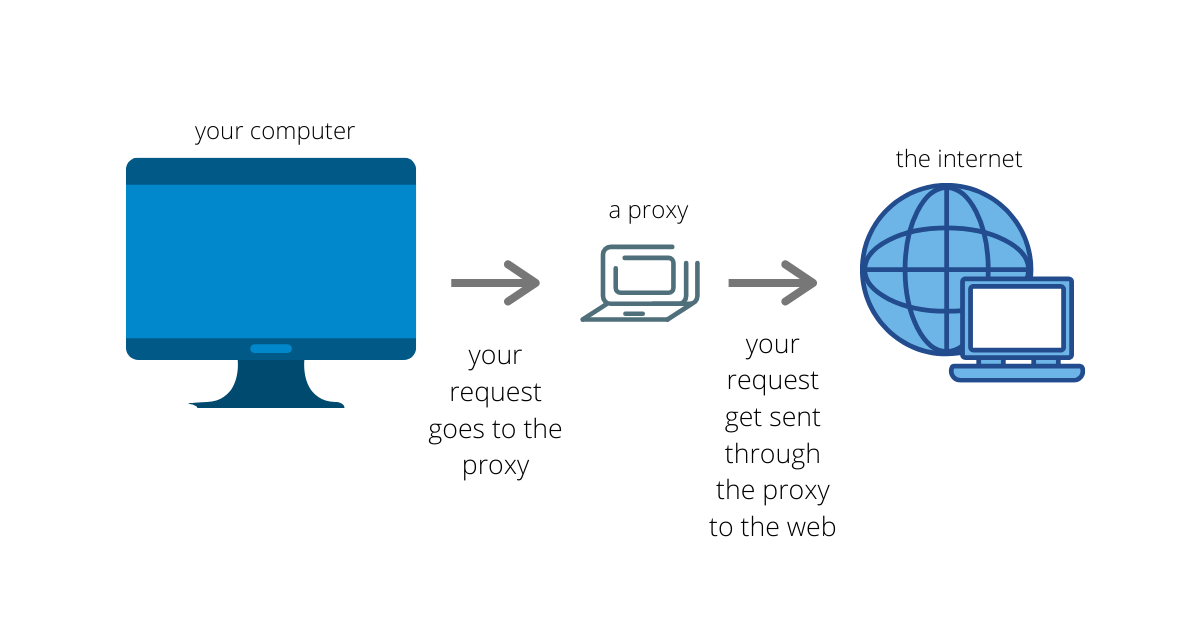
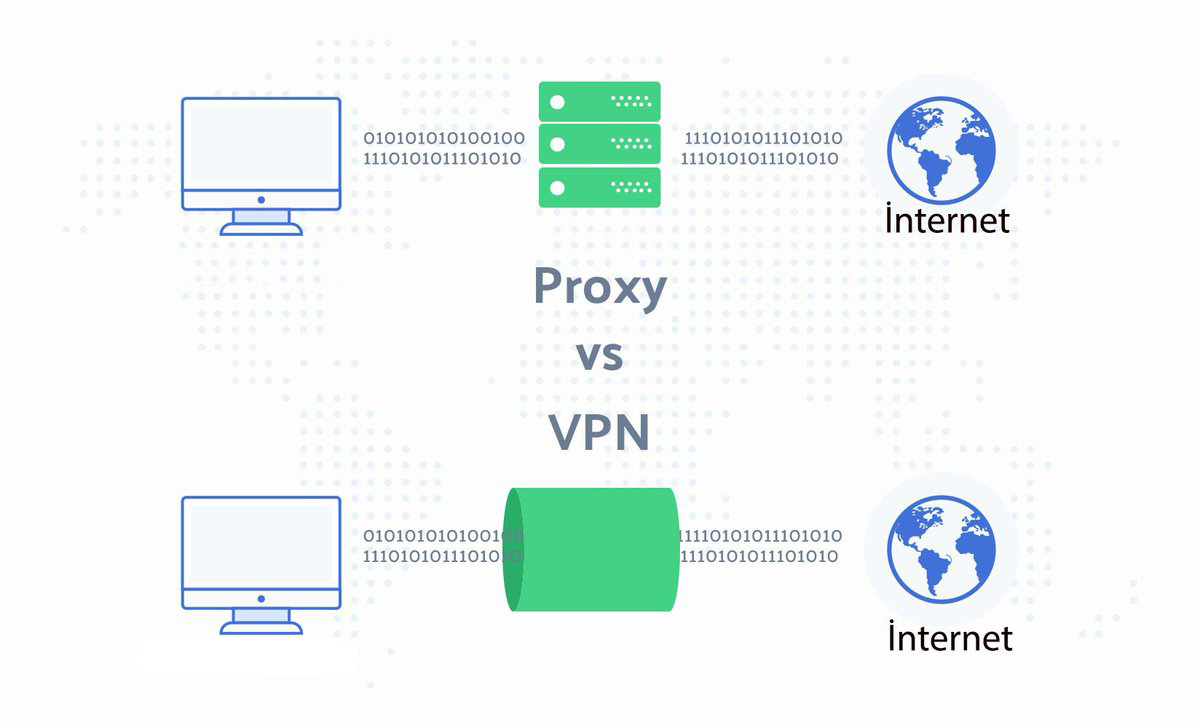
In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource.[1]
Instead of connecting directly to a server that can fulfill a request for a resource, such as a file or web page, the client directs the request to the proxy server, which evaluates the request and performs the required network transactions. This serves as a method to simplify or control the complexity of the request, or provide additional benefits such as load balancing, privacy, or security. Proxies were devised to add structure and encapsulation to distributed systems.[2] A proxy server thus functions on behalf of the client when requesting service, potentially masking the true origin of the request to the resource server.
Types[edit]
A proxy server may reside on the user’s local computer, or at any point between the user’s computer and destination servers on the Internet. A proxy server that passes unmodified requests and responses is usually called a gateway or sometimes a tunneling proxy. A forward proxy is an Internet-facing proxy used to retrieve data from a wide range of sources (in most cases anywhere on the Internet). A reverse proxy is usually an internal-facing proxy used as a front-end to control and protect access to a server on a private network. A reverse proxy commonly also performs tasks such as load-balancing, authentication, decryption and caching.[3]
Open proxies[edit]
An open proxy forwarding requests from and to anywhere on the Internet.
An open proxy is a forwarding proxy server that is accessible by any Internet user. In 2008, network security expert Gordon Lyon estimated that «hundreds of thousands» of open proxies are operated on the Internet.[4]
- Anonymous proxy – This server reveals its identity as a proxy server but does not disclose the originating IP address of the client. Although this type of server can be discovered easily, it can be beneficial for some users as it hides the originating IP address.
- Transparent proxy – This server not only identifies itself as a proxy server but with the support of HTTP header fields such as
X-Forwarded-For, the originating IP address can be retrieved as well. The main benefit of using this type of server is its ability to cache a website for faster retrieval.
Reverse proxies[edit]
A reverse proxy taking requests from the Internet and forwarding them to servers in an internal network. Those making requests connect to the proxy and may not be aware of the internal network.
A reverse proxy (or surrogate) is a proxy server that appears to clients to be an ordinary server. Reverse proxies forward requests to one or more ordinary servers that handle the request. The response from the proxy server is returned as if it came directly from the original server, leaving the client with no knowledge of the original server.[5] Reverse proxies are installed in the neighborhood of one or more web servers. All traffic coming from the Internet and with a destination of one of the neighborhood’s web servers goes through the proxy server. The use of reverse originates in its counterpart forward proxy since the reverse proxy sits closer to the web server and serves only a restricted set of websites. There are several reasons for installing reverse proxy servers:
- Encryption/SSL acceleration: when secure websites are created, the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption is often not done by the web server itself, but by a reverse proxy that is equipped with SSL acceleration hardware. Furthermore, a host can provide a single «SSL proxy» to provide SSL encryption for an arbitrary number of hosts, removing the need for a separate SSL server certificate for each host, with the downside that all hosts behind the SSL proxy have to share a common DNS name or IP address for SSL connections. This problem can partly be overcome by using the SubjectAltName feature of X.509 certificates or the SNI extension of TLS.
- Load balancing: the reverse proxy can distribute the load to several web servers, each web server serving its own application area. In such a case, the reverse proxy may need to rewrite the URLs in each web page (translation from externally known URLs to the internal locations).
- Serve/cache static content: A reverse proxy can offload the web servers by caching static content like pictures and other static graphical content.
- Compression: the proxy server can optimize and compress the content to speed up the load time.
- Spoon feeding: reduces resource usage caused by slow clients on the web servers by caching the content the web server sent and slowly «spoon feeding» it to the client. This especially benefits dynamically generated pages.
- Security: the proxy server is an additional layer of defense and can protect against some OS and web-server-specific attacks. However, it does not provide any protection from attacks against the web application or service itself, which is generally considered the larger threat.
- Extranet publishing: a reverse proxy server facing the Internet can be used to communicate to a firewall server internal to an organization, providing extranet access to some functions while keeping the servers behind the firewalls. If used in this way, security measures should be considered to protect the rest of your infrastructure in case this server is compromised, as its web application is exposed to attack from the Internet.
Uses[edit]
Monitoring and filtering[edit]
Content-control software[edit]
A content-filtering web proxy server provides administrative control over the content that may be relayed in one or both directions through the proxy. It is commonly used in both commercial and non-commercial organizations (especially schools) to ensure that Internet usage conforms to acceptable use policy.
Content filtering proxy servers will often support user authentication to control web access. It also usually produces logs, either to give detailed information about the URLs accessed by specific users or to monitor bandwidth usage statistics. It may also communicate to daemon-based and/or ICAP-based antivirus software to provide security against viruses and other malware by scanning incoming content in real-time before it enters the network.
Many workplaces, schools, and colleges restrict web sites and online services that are accessible and available in their buildings. Governments also censor undesirable content. This is done either with a specialized proxy, called a content filter (both commercial and free products are available), or by using a cache-extension protocol such as ICAP, that allows plug-in extensions to an open caching architecture.
Websites commonly used by students to circumvent filters and access blocked content often include a proxy, from which the user can then access the websites that the filter is trying to block.
Requests may be filtered by several methods, such as a URL or DNS blacklists, URL regex filtering, MIME filtering, or content keyword filtering. Blacklists are often provided and maintained by web-filtering companies, often grouped into categories (pornography, gambling, shopping, social networks, etc..).
Assuming the requested URL is acceptable, the content is then fetched by the proxy. At this point, a dynamic filter may be applied on the return path. For example, JPEG files could be blocked based on fleshtone matches, or language filters could dynamically detect unwanted language. If the content is rejected then an HTTP fetch error may be returned to the requester.
Most web filtering companies use an internet-wide crawling robot that assesses the likelihood that content is a certain type. The resultant database is then corrected by manual labor based on complaints or known flaws in the content-matching algorithms.
Some proxies scan outbound content, e.g., for data loss prevention; or scan content for malicious software.
Filtering of encrypted data[edit]
Web filtering proxies are not able to peer inside secure sockets HTTP transactions, assuming the chain-of-trust of SSL/TLS (Transport Layer Security) has not been tampered with. The SSL/TLS chain-of-trust relies on trusted root certificate authorities.
In a workplace setting where the client is managed by the organization, devices may be configured to trust a root certificate whose private key is known to the proxy. In such situations, proxy analysis of the contents of an SSL/TLS transaction becomes possible. The proxy is effectively operating a man-in-the-middle attack, allowed by the client’s trust of a root certificate the proxy owns.
Bypassing filters and censorship[edit]
If the destination server filters content based on the origin of the request, the use of a proxy can circumvent this filter. For example, a server using IP-based geolocation to restrict its service to a certain country can be accessed using a proxy located in that country to access the service.[6]: 3
Web proxies are the most common means of bypassing government censorship, although no more than 3% of Internet users use any circumvention tools.[6]: 7
Some proxy service providers allow businesses access to their proxy network for rerouting traffic for business intelligence purposes.[7]
In some cases, users can circumvent proxies which filter using blacklists using services designed to proxy information from a non-blacklisted location.[8]
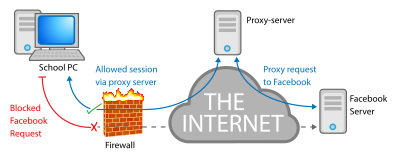
Many schools block access to popular websites such as Facebook. Students can use proxy servers to circumvent this security. However, by connecting to proxy servers, they might be opening themselves up to danger by passing sensitive information such as personal photos and passwords through the proxy server. Some content filters block proxy servers in order to keep users from using them to bypass the filter.
Logging and eavesdropping[edit]
Proxies can be installed in order to eavesdrop upon the data-flow between client machines and the web. All content sent or accessed – including passwords submitted and cookies used – can be captured and analyzed by the proxy operator. For this reason, passwords to online services (such as webmail and banking) should always be exchanged over a cryptographically secured connection, such as SSL.
By chaining the proxies which do not reveal data about the original requester, it is possible to obfuscate activities from the eyes of the user’s destination. However, more traces will be left on the intermediate hops, which could be used or offered up to trace the user’s activities. If the policies and administrators of these other proxies are unknown, the user may fall victim to a false sense of security just because those details are out of sight and mind.
In what is more of an inconvenience than a risk, proxy users may find themselves being blocked from certain Web sites, as numerous forums and Web sites block IP addresses from proxies known to have spammed or trolled the site. Proxy bouncing can be used to maintain privacy.
Improving performance[edit]
A caching proxy server accelerates service requests by retrieving the content saved from a previous request made by the same client or even other clients. Caching proxies keep local copies of frequently requested resources, allowing large organizations to significantly reduce their upstream bandwidth usage and costs, while significantly increasing performance. Most ISPs and large businesses have a caching proxy. Caching proxies were the first kind of proxy server. Web proxies are commonly used to cache web pages from a web server.[9] Poorly implemented caching proxies can cause problems, such as an inability to use user authentication.[10]
A proxy that is designed to mitigate specific link related issues or degradation is a Performance Enhancing Proxy (PEPs). These are typically used to improve TCP performance in the presence of high round-trip times or high packet loss (such as wireless or mobile phone networks); or highly asymmetric links featuring very different upload and download rates. PEPs can make more efficient use of the network, for example, by merging TCP ACKs (acknowledgements) or compressing data sent at the application layer.[11]
Translation[edit]
A translation proxy is a proxy server that is used to localize a website experience for different markets. Traffic from the global audience is routed through the translation proxy to the source website. As visitors browse the proxied site, requests go back to the source site where pages are rendered. The original language content in the response is replaced by the translated content as it passes back through the proxy. The translations used in a translation proxy can be either machine translation, human translation, or a combination of machine and human translation. Different translation proxy implementations have different capabilities. Some allow further customization of the source site for the local audiences such as excluding the source content or substituting the source content with the original local content.
Repairing errors[edit]
A proxy can be used to automatically repair errors in the proxied content. For instance, the BikiniProxy system instruments JavaScript code on the fly in order to detect and automatically repair errors happening in the browser.[12] Another kind of repair that can be done by a proxy is to fix accessibility issues.[13]
Accessing services anonymously[edit]
An anonymous proxy server (sometimes called a web proxy) generally attempts to anonymize web surfing. Anonymizers may be differentiated into several varieties. The destination server (the server that ultimately satisfies the web request) receives requests from the anonymizing proxy server and thus does not receive information about the end user’s address. The requests are not anonymous to the anonymizing proxy server, however, and so a degree of trust is present between the proxy server and the user. Many proxy servers are funded through a continued advertising link to the user.
Access control: Some proxy servers implement a logon requirement. In large organizations, authorized users must log on to gain access to the web. The organization can thereby track usage to individuals. Some anonymizing proxy servers may forward data packets with header lines such as HTTP_VIA, HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR, or HTTP_FORWARDED, which may reveal the IP address of the client. Other anonymizing proxy servers, known as elite or high-anonymity proxies, make it appear that the proxy server is the client. A website could still suspect a proxy is being used if the client sends packets that include a cookie from a previous visit that did not use the high-anonymity proxy server. Clearing cookies, and possibly the cache, would solve this problem.
QA geotargeted advertising[edit]
Advertisers use proxy servers for validating, checking and quality assurance of geotargeted ads. A geotargeting ad server checks the request source IP address and uses a geo-IP database to determine the geographic source of requests.[14] Using a proxy server that is physically located inside a specific country or a city gives advertisers the ability to test geotargeted ads.
Security[edit]
A proxy can keep the internal network structure of a company secret by using network address translation, which can help the security of the internal network.[15] This makes requests from machines and users on the local network anonymous. Proxies can also be combined with firewalls.
An incorrectly configured proxy can provide access to a network otherwise isolated from the Internet.[4]
Cross-domain resources[edit]
Proxies allow web sites to make web requests to externally hosted resources (e.g. images, music files, etc.) when cross-domain restrictions prohibit the web site from linking directly to the outside domains. Proxies also allow the browser to make web requests to externally hosted content on behalf of a website when cross-domain restrictions (in place to protect websites from the likes of data theft) prohibit the browser from directly accessing the outside domains.
Malicious usages[edit]
Secondary market brokers[edit]
Secondary market brokers use web proxy servers to circumvent restrictions on online purchase of limited products such as limited sneakers[16] or tickets.
Implementations of proxies[edit]
Web proxy servers[edit]
Web proxies forward HTTP requests. The request from the client is the same as a regular HTTP request except the full URL is passed, instead of just the path.[17]
GET https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proxy_server HTTP/1.1 Proxy-Authorization: Basic encoded-credentials Accept: text/html
This request is sent to the proxy server, the proxy makes the request specified and returns the response.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: text/html; charset UTF-8
Some web proxies allow the HTTP CONNECT method to set up forwarding of arbitrary data through the connection; a common policy is to only forward port 443 to allow HTTPS traffic.
Examples of web proxy servers include Apache (with mod_proxy or Traffic Server), HAProxy, IIS configured as proxy (e.g., with Application Request Routing), Nginx, Privoxy, Squid, Varnish (reverse proxy only), WinGate, Ziproxy, Tinyproxy, RabbIT and Polipo.
For clients, the problem of complex or multiple proxy-servers is solved by a client-server Proxy auto-config protocol (PAC file).
SOCKS proxy[edit]
SOCKS also forwards arbitrary data after a connection phase, and is similar to HTTP CONNECT in web proxies.
Transparent proxy[edit]
Also known as an intercepting proxy, inline proxy, or forced proxy, a transparent proxy intercepts normal application layer communication without requiring any special client configuration. Clients need not be aware of the existence of the proxy. A transparent proxy is normally located between the client and the Internet, with the proxy performing some of the functions of a gateway or router.[18]
RFC 2616 (Hypertext Transfer Protocol—HTTP/1.1) offers standard definitions:
«A ‘transparent proxy’ is a proxy that does not modify the request or response beyond what is required for proxy authentication and identification». «A ‘non-transparent proxy’ is a proxy that modifies the request or response in order to provide some added service to the user agent, such as group annotation services, media type transformation, protocol reduction, or anonymity filtering».
TCP Intercept is a traffic filtering security feature that protects TCP servers from TCP SYN flood attacks, which are a type of denial-of-service attack. TCP Intercept is available for IP traffic only.
In 2009 a security flaw in the way that transparent proxies operate was published by Robert Auger,[19] and the Computer Emergency Response Team issued an advisory listing dozens of affected transparent and intercepting proxy servers.[20]
Purpose[edit]
Intercepting proxies are commonly used in businesses to enforce acceptable use policy, and to ease administrative overheads since no client browser configuration is required. This second reason however is mitigated by features such as Active Directory group policy, or DHCP and automatic proxy detection.
Intercepting proxies are also commonly used by ISPs in some countries to save upstream bandwidth and improve customer response times by caching. This is more common in countries where bandwidth is more limited (e.g. island nations) or must be paid for.
Issues[edit]
The diversion/interception of a TCP connection creates several issues. First, the original destination IP and port must somehow be communicated to the proxy. This is not always possible (e.g., where the gateway and proxy reside on different hosts). There is a class of cross-site attacks that depend on certain behavior of intercepting proxies that do not check or have access to information about the original (intercepted) destination. This problem may be resolved by using an integrated packet-level and application level appliance or software which is then able to communicate this information between the packet handler and the proxy.
Intercepting also creates problems for HTTP authentication, especially connection-oriented authentication such as NTLM, as the client browser believes it is talking to a server rather than a proxy. This can cause problems where an intercepting proxy requires authentication, then the user connects to a site that also requires authentication.
Finally, intercepting connections can cause problems for HTTP caches, as some requests and responses become uncacheable by a shared cache.
Implementation methods[edit]
In integrated firewall/proxy servers where the router/firewall is on the same host as the proxy, communicating original destination information can be done by any method, for example Microsoft TMG or WinGate.
Interception can also be performed using Cisco’s WCCP (Web Cache Control Protocol). This proprietary protocol resides on the router and is configured from the cache, allowing the cache to determine what ports and traffic is sent to it via transparent redirection from the router. This redirection can occur in one of two ways: GRE tunneling (OSI Layer 3) or MAC rewrites (OSI Layer 2).
Once traffic reaches the proxy machine itself interception is commonly performed with NAT (Network Address Translation). Such setups are invisible to the client browser, but leave the proxy visible to the web server and other devices on the internet side of the proxy. Recent Linux and some BSD releases provide TPROXY (transparent proxy) which performs IP-level (OSI Layer 3) transparent interception and spoofing of outbound traffic, hiding the proxy IP address from other network devices.
Detection[edit]
Several methods may be used to detect the presence of an intercepting proxy server:
- By comparing the client’s external IP address to the address seen by an external web server, or sometimes by examining the HTTP headers received by a server. A number of sites have been created to address this issue, by reporting the user’s IP address as seen by the site back to the user on a web page. Google also returns the IP address as seen by the page if the user searches for «IP».
- By comparing the result of online IP checkers when accessed using HTTPS vs HTTP, as most intercepting proxies do not intercept SSL. If there is suspicion of SSL being intercepted, one can examine the certificate associated with any secure web site, the root certificate should indicate whether it was issued for the purpose of intercepting.
- By comparing the sequence of network hops reported by a tool such as traceroute for a proxied protocol such as HTTP (port 80) with that for a non-proxied protocol such as SMTP (port 25).[21]
- By attempting to make a connection to an IP address at which there is known to be no server. The proxy will accept the connection and then attempt to proxy it on. When the proxy finds no server to accept the connection it may return an error message or simply close the connection to the client. This difference in behavior is simple to detect. For example, most web browsers will generate a browser created error page in the case where they cannot connect to an HTTP server but will return a different error in the case where the connection is accepted and then closed.[22]
- By serving the end-user specially programmed Adobe Flash SWF applications or Sun Java applets that send HTTP calls back to their server.
CGI proxy[edit]
A CGI web proxy accepts target URLs using a Web form in the user’s browser window, processes the request, and returns the results to the user’s browser. Consequently, it can be used on a device or network that does not allow «true» proxy settings to be changed. The first recorded CGI proxy, named «rover» at the time but renamed in 1998 to «CGIProxy»,[23] was developed by American computer scientist James Marshall in early 1996 for an article in «Unix Review» by Rich Morin.[24]
The majority of CGI proxies are powered by one of CGIProxy (written in the Perl language), Glype (written in the PHP language), or PHProxy (written in the PHP language). As of April 2016, CGIProxy has received about 2 million downloads, Glype has received almost a million downloads,[25] whilst PHProxy still receives hundreds of downloads per week.[26] Despite waning in popularity[27] due to VPNs and other privacy methods, as of September 2021 there are still a few hundred CGI proxies online.[28]
Some CGI proxies were set up for purposes such as making websites more accessible to disabled people, but have since been shut down due to excessive traffic, usually caused by a third party advertising the service as a means to bypass local filtering. Since many of these users don’t care about the collateral damage they are causing, it became necessary for organizations to hide their proxies, disclosing the URLs only to those who take the trouble to contact the organization and demonstrate a genuine need.[29]
Suffix proxy[edit]
A suffix proxy allows a user to access web content by appending the name of the proxy server to the URL of the requested content (e.g. «en.wikipedia.org.SuffixProxy.com«). Suffix proxy servers are easier to use than regular proxy servers but they do not offer high levels of anonymity and their primary use is for bypassing web filters. However, this is rarely used due to more advanced web filters.
Tor onion proxy software[edit]
Tor is a system intended to provide online anonymity.[30] Tor client software routes Internet traffic through a worldwide volunteer network of servers for concealing a user’s computer location or usage from someone conducting network surveillance or traffic analysis. Using Tor makes tracing Internet activity more difficult,[30] and is intended to protect users’ personal freedom and their online privacy.
«Onion routing» refers to the layered nature of the encryption service: The original data are encrypted and re-encrypted multiple times, then sent through successive Tor relays, each one of which decrypts a «layer» of encryption before passing the data on to the next relay and ultimately the destination. This reduces the possibility of the original data being unscrambled or understood in transit.[31]
I2P anonymous proxy[edit]
The I2P anonymous network (‘I2P’) is a proxy network aiming at online anonymity. It implements garlic routing, which is an enhancement of Tor’s onion routing. I2P is fully distributed and works by encrypting all communications in various layers and relaying them through a network of routers run by volunteers in various locations. By keeping the source of the information hidden, I2P offers censorship resistance. The goals of I2P are to protect users’ personal freedom, privacy, and ability to conduct confidential business.
Each user of I2P runs an I2P router on their computer (node). The I2P router takes care of finding other peers and building anonymizing tunnels through them. I2P provides proxies for all protocols (HTTP, IRC, SOCKS, …).
Comparison to network address translators[edit]
The proxy concept refers to a layer 7 application in the OSI reference model. Network address translation (NAT) is similar to a proxy but operates in layer 3.
In the client configuration of layer-3 NAT, configuring the gateway is sufficient. However, for the client configuration of a layer 7 proxy, the destination of the packets that the client generates must always be the proxy server (layer 7), then the proxy server reads each packet and finds out the true destination.
Because NAT operates at layer-3, it is less resource-intensive than the layer-7 proxy, but also less flexible. As we compare these two technologies, we might encounter a terminology known as ‘transparent firewall’. Transparent firewall means that the proxy uses the layer-7 proxy advantages without the knowledge of the client. The client presumes that the gateway is a NAT in layer 3, and it does not have any idea about the inside of the packet, but through this method, the layer-3 packets are sent to the layer-7 proxy for investigation.
DNS proxy[edit]
A DNS proxy server takes DNS queries from a (usually local) network and forwards them to an Internet Domain Name Server. It may also cache DNS records.
Proxifiers[edit]
Some client programs «SOCKS-ify» requests,[32] which allows adaptation of any networked software to connect to external networks via certain types of proxy servers (mostly SOCKS).
Residential proxy[edit]
A residential proxy is an intermediary that uses a real IP address provided by an Internet Service Provider (ISP) with physical devices such as mobiles and computers of end-users. Instead of connecting directly to a server, residential proxy users connect to the target through residential IP addresses. The target then identifies them as organic internet users. It does not let any tracking tool identify the reallocation of the user. Any residential proxy can send any number of concurrent requests and IP addresses are directly related to a specific region.[33] Unlike regular residential proxies, which hide user’s real IP address behind another IP address, rotating residential proxies, also known as backconnect proxies, conceal user’s real IP address behind a pool of proxies. These proxies switch between themselves with every session or at regular intervals.[34]
See also[edit]
- InterPlanetary File System — makes proxy servers redundant
- Application firewall
- Captive portal
- Darknet
- Distributed Checksum Clearinghouse
- FreeProxy
- Internet privacy
- Proxy list
- SMTP proxy
- SOCKS an alternative firewall traversal protocol supported by many applications
- Web accelerator which discusses host-based HTTP acceleration
- Web cache
References[edit]
- ^ World-Wide Web Proxies, Ari Luotonen, April 1994
- ^ Shapiro, Marc (May 1986). Structure and Encapsulation in Distributed Systems: the Proxy Principle. 6th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS). Cambridge, MA, USA. pp. 198–204. inria-00444651.
- ^ «Proxy servers and tunneling». MDN Web Docs. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ a b Lyon, Gordon (2008). Nmap network scanning. US: Insecure. p. 270. ISBN 978-0-9799587-1-7.
- ^ «Forward and Reverse Proxies». httpd mod_proxy. Apache. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- ^ a b «2010 Circumvention Tool Usage Report» (PDF). The Berkman Center for Internet & Society at Harvard University. October 2010.
- ^ «How to Check if Website is Down or Working Worldwide». Hostinger. 19 November 2019. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ^ «Using a Ninjaproxy to get through a filtered proxy». advanced filtering mechanics. TSNP. Archived from the original on 9 March 2016. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ Thomas, Keir (2006). Beginning Ubuntu Linux: From Novice to Professional. Apress. ISBN 978-1-59059-627-2.
A proxy server helps speed up Internet access by storing frequently accessed pages
- ^ I. Cooper; J. Dilley (June 2001). Known HTTP Proxy/Caching Problems. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC3143. RFC 3143. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ^ «Layering». Performance Enhancing Proxies Intended to Mitigate Link-Related Degradations. IETF. June 2001. p. 4. sec. 2.1. doi:10.17487/RFC3135. RFC 3135. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- ^ Durieux, T.; Hamadi, Y.; Monperrus, M. (2018). «Fully Automated HTML and JavaScript Rewriting for Constructing a Self-Healing Web Proxy». 2018 IEEE 29th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE). 2018 IEEE 29th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE). pp. 1–12. arXiv:1803.08725. doi:10.1109/ISSRE.2018.00012. ISBN 978-1-5386-8321-7. S2CID 4268784.
- ^ Zhang, Xiaoyi; Ross, Anne Spencer; Caspi, Anat; Fogarty, James; Wobbrock, Jacob O. (2017). «Interaction Proxies for Runtime Repair and Enhancement of Mobile Application Accessibility». Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. pp. 6024–6037. doi:10.1145/3025453.3025846. ISBN 9781450346559. S2CID 20937177.
- ^ «Hot Tactics For Geo-Targeted Ads on Google & Bing». October 2013. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «Firewall and Proxy Server HOWTO». tldp.org. Retrieved 4 September 2011.
The proxy server is, above all, a security device.
- ^ «Sneaker Bot Supreme Proxy». GeoSurf. Retrieved 24 September 2017.
- ^ «absolute-form». HTTP/1.1 Message Syntax and Routing. IETF. June 2014. p. 41. sec. 5.3.2. doi:10.17487/RFC7230. RFC 7230. Retrieved 4 November 2017.
a client MUST send the target URI in absolute-form as the request-target
- ^ «Transparent Proxy Definition». ukproxyserver.org. 1 February 2011. Archived from the original on 1 March 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2013.
- ^ «Socket Capable Browser Plugins Result in Transparent Proxy Abuse». The Security Practice. 9 March 2009. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- ^ «Vulnerability Note VU#435052». US CERT. 23 February 2009. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- ^ «Subversion Dev: Transparent Proxy detection (was Re: Introduction_». Tracetop.sourceforge.net. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ Wessels, Duane (2004). Squid The Definitive Guide. O’Reilly. pp. 130. ISBN 978-0-596-00162-9.
- ^ Marshall, James. «CGIProxy». Retrieved 12 November 2018.
- ^ «The Limits of Control». June 1996. Retrieved 12 November 2018.
- ^ «Glype® Proxy Script». glype.com. Archived from the original on 3 January 2013. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ^ «PHProxy». SourceForge.
- ^ «Google Trends». Google Trends.
- ^ «Proxy Stats :: Get Proxi.es». getproxi.es. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- ^ Estrada-Jiménez, José (March 2017). «Online advertising: Analysis of privacy threats and protection approaches». Computer Communications. 100: 32–51. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2016.12.016. hdl:2117/99742.
- ^ a b Glater, Jonathan (25 January 2006). «Privacy for People Who Don’t Show Their Navels». The New York Times. Retrieved 4 August 2011.
- ^ The Tor Project. «Tor: anonymity online». Retrieved 9 January 2011.
- ^ Zwicky, Elizabeth D.; Cooper, Simon; Chapman, D. Brent (2000). Building Internet Firewalls (2nd ed.). p. 235. ISBN 978-1-56592-871-8.
- ^ Smith, Vincent (2019). Go Web Scraping Quick Start Guide: Implement the power of Go to scrape and crawl data from the web. Packt Publishing Ltd. ISBN 978-1-78961-294-3.
- ^ Keenan, James. «What are Residential Proxies?». Smartproxy.com. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
External links[edit]
- Proxy software and scripts at Curlie
- Free web-based proxy services at Curlie
- Free http proxy servers at Curlie
For Wikipedia’s policy on editing from open proxies, please see Wikipedia:Open proxies. For other uses, see Proxy.
Communication between two computers connected through a third computer acting as a proxy server. This can protect Alice’s privacy, as Bob only knows about the proxy and cannot identify or contact Alice directly.
In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application that acts as an intermediary between a client requesting a resource and the server providing that resource.[1]
Instead of connecting directly to a server that can fulfill a request for a resource, such as a file or web page, the client directs the request to the proxy server, which evaluates the request and performs the required network transactions. This serves as a method to simplify or control the complexity of the request, or provide additional benefits such as load balancing, privacy, or security. Proxies were devised to add structure and encapsulation to distributed systems.[2] A proxy server thus functions on behalf of the client when requesting service, potentially masking the true origin of the request to the resource server.
Types[edit]
A proxy server may reside on the user’s local computer, or at any point between the user’s computer and destination servers on the Internet. A proxy server that passes unmodified requests and responses is usually called a gateway or sometimes a tunneling proxy. A forward proxy is an Internet-facing proxy used to retrieve data from a wide range of sources (in most cases anywhere on the Internet). A reverse proxy is usually an internal-facing proxy used as a front-end to control and protect access to a server on a private network. A reverse proxy commonly also performs tasks such as load-balancing, authentication, decryption and caching.[3]
Open proxies[edit]
An open proxy forwarding requests from and to anywhere on the Internet.
An open proxy is a forwarding proxy server that is accessible by any Internet user. In 2008, network security expert Gordon Lyon estimated that «hundreds of thousands» of open proxies are operated on the Internet.[4]
- Anonymous proxy – This server reveals its identity as a proxy server but does not disclose the originating IP address of the client. Although this type of server can be discovered easily, it can be beneficial for some users as it hides the originating IP address.
- Transparent proxy – This server not only identifies itself as a proxy server but with the support of HTTP header fields such as
X-Forwarded-For, the originating IP address can be retrieved as well. The main benefit of using this type of server is its ability to cache a website for faster retrieval.
Reverse proxies[edit]
A reverse proxy taking requests from the Internet and forwarding them to servers in an internal network. Those making requests connect to the proxy and may not be aware of the internal network.
A reverse proxy (or surrogate) is a proxy server that appears to clients to be an ordinary server. Reverse proxies forward requests to one or more ordinary servers that handle the request. The response from the proxy server is returned as if it came directly from the original server, leaving the client with no knowledge of the original server.[5] Reverse proxies are installed in the neighborhood of one or more web servers. All traffic coming from the Internet and with a destination of one of the neighborhood’s web servers goes through the proxy server. The use of reverse originates in its counterpart forward proxy since the reverse proxy sits closer to the web server and serves only a restricted set of websites. There are several reasons for installing reverse proxy servers:
- Encryption/SSL acceleration: when secure websites are created, the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) encryption is often not done by the web server itself, but by a reverse proxy that is equipped with SSL acceleration hardware. Furthermore, a host can provide a single «SSL proxy» to provide SSL encryption for an arbitrary number of hosts, removing the need for a separate SSL server certificate for each host, with the downside that all hosts behind the SSL proxy have to share a common DNS name or IP address for SSL connections. This problem can partly be overcome by using the SubjectAltName feature of X.509 certificates or the SNI extension of TLS.
- Load balancing: the reverse proxy can distribute the load to several web servers, each web server serving its own application area. In such a case, the reverse proxy may need to rewrite the URLs in each web page (translation from externally known URLs to the internal locations).
- Serve/cache static content: A reverse proxy can offload the web servers by caching static content like pictures and other static graphical content.
- Compression: the proxy server can optimize and compress the content to speed up the load time.
- Spoon feeding: reduces resource usage caused by slow clients on the web servers by caching the content the web server sent and slowly «spoon feeding» it to the client. This especially benefits dynamically generated pages.
- Security: the proxy server is an additional layer of defense and can protect against some OS and web-server-specific attacks. However, it does not provide any protection from attacks against the web application or service itself, which is generally considered the larger threat.
- Extranet publishing: a reverse proxy server facing the Internet can be used to communicate to a firewall server internal to an organization, providing extranet access to some functions while keeping the servers behind the firewalls. If used in this way, security measures should be considered to protect the rest of your infrastructure in case this server is compromised, as its web application is exposed to attack from the Internet.
Uses[edit]
Monitoring and filtering[edit]
Content-control software[edit]
A content-filtering web proxy server provides administrative control over the content that may be relayed in one or both directions through the proxy. It is commonly used in both commercial and non-commercial organizations (especially schools) to ensure that Internet usage conforms to acceptable use policy.
Content filtering proxy servers will often support user authentication to control web access. It also usually produces logs, either to give detailed information about the URLs accessed by specific users or to monitor bandwidth usage statistics. It may also communicate to daemon-based and/or ICAP-based antivirus software to provide security against viruses and other malware by scanning incoming content in real-time before it enters the network.
Many workplaces, schools, and colleges restrict web sites and online services that are accessible and available in their buildings. Governments also censor undesirable content. This is done either with a specialized proxy, called a content filter (both commercial and free products are available), or by using a cache-extension protocol such as ICAP, that allows plug-in extensions to an open caching architecture.
Websites commonly used by students to circumvent filters and access blocked content often include a proxy, from which the user can then access the websites that the filter is trying to block.
Requests may be filtered by several methods, such as a URL or DNS blacklists, URL regex filtering, MIME filtering, or content keyword filtering. Blacklists are often provided and maintained by web-filtering companies, often grouped into categories (pornography, gambling, shopping, social networks, etc..).
Assuming the requested URL is acceptable, the content is then fetched by the proxy. At this point, a dynamic filter may be applied on the return path. For example, JPEG files could be blocked based on fleshtone matches, or language filters could dynamically detect unwanted language. If the content is rejected then an HTTP fetch error may be returned to the requester.
Most web filtering companies use an internet-wide crawling robot that assesses the likelihood that content is a certain type. The resultant database is then corrected by manual labor based on complaints or known flaws in the content-matching algorithms.
Some proxies scan outbound content, e.g., for data loss prevention; or scan content for malicious software.
Filtering of encrypted data[edit]
Web filtering proxies are not able to peer inside secure sockets HTTP transactions, assuming the chain-of-trust of SSL/TLS (Transport Layer Security) has not been tampered with. The SSL/TLS chain-of-trust relies on trusted root certificate authorities.
In a workplace setting where the client is managed by the organization, devices may be configured to trust a root certificate whose private key is known to the proxy. In such situations, proxy analysis of the contents of an SSL/TLS transaction becomes possible. The proxy is effectively operating a man-in-the-middle attack, allowed by the client’s trust of a root certificate the proxy owns.
Bypassing filters and censorship[edit]
If the destination server filters content based on the origin of the request, the use of a proxy can circumvent this filter. For example, a server using IP-based geolocation to restrict its service to a certain country can be accessed using a proxy located in that country to access the service.[6]: 3
Web proxies are the most common means of bypassing government censorship, although no more than 3% of Internet users use any circumvention tools.[6]: 7
Some proxy service providers allow businesses access to their proxy network for rerouting traffic for business intelligence purposes.[7]
In some cases, users can circumvent proxies which filter using blacklists using services designed to proxy information from a non-blacklisted location.[8]
Many schools block access to popular websites such as Facebook. Students can use proxy servers to circumvent this security. However, by connecting to proxy servers, they might be opening themselves up to danger by passing sensitive information such as personal photos and passwords through the proxy server. Some content filters block proxy servers in order to keep users from using them to bypass the filter.
Logging and eavesdropping[edit]
Proxies can be installed in order to eavesdrop upon the data-flow between client machines and the web. All content sent or accessed – including passwords submitted and cookies used – can be captured and analyzed by the proxy operator. For this reason, passwords to online services (such as webmail and banking) should always be exchanged over a cryptographically secured connection, such as SSL.
By chaining the proxies which do not reveal data about the original requester, it is possible to obfuscate activities from the eyes of the user’s destination. However, more traces will be left on the intermediate hops, which could be used or offered up to trace the user’s activities. If the policies and administrators of these other proxies are unknown, the user may fall victim to a false sense of security just because those details are out of sight and mind.
In what is more of an inconvenience than a risk, proxy users may find themselves being blocked from certain Web sites, as numerous forums and Web sites block IP addresses from proxies known to have spammed or trolled the site. Proxy bouncing can be used to maintain privacy.
Improving performance[edit]
A caching proxy server accelerates service requests by retrieving the content saved from a previous request made by the same client or even other clients. Caching proxies keep local copies of frequently requested resources, allowing large organizations to significantly reduce their upstream bandwidth usage and costs, while significantly increasing performance. Most ISPs and large businesses have a caching proxy. Caching proxies were the first kind of proxy server. Web proxies are commonly used to cache web pages from a web server.[9] Poorly implemented caching proxies can cause problems, such as an inability to use user authentication.[10]
A proxy that is designed to mitigate specific link related issues or degradation is a Performance Enhancing Proxy (PEPs). These are typically used to improve TCP performance in the presence of high round-trip times or high packet loss (such as wireless or mobile phone networks); or highly asymmetric links featuring very different upload and download rates. PEPs can make more efficient use of the network, for example, by merging TCP ACKs (acknowledgements) or compressing data sent at the application layer.[11]
Translation[edit]
A translation proxy is a proxy server that is used to localize a website experience for different markets. Traffic from the global audience is routed through the translation proxy to the source website. As visitors browse the proxied site, requests go back to the source site where pages are rendered. The original language content in the response is replaced by the translated content as it passes back through the proxy. The translations used in a translation proxy can be either machine translation, human translation, or a combination of machine and human translation. Different translation proxy implementations have different capabilities. Some allow further customization of the source site for the local audiences such as excluding the source content or substituting the source content with the original local content.
Repairing errors[edit]
A proxy can be used to automatically repair errors in the proxied content. For instance, the BikiniProxy system instruments JavaScript code on the fly in order to detect and automatically repair errors happening in the browser.[12] Another kind of repair that can be done by a proxy is to fix accessibility issues.[13]
Accessing services anonymously[edit]
An anonymous proxy server (sometimes called a web proxy) generally attempts to anonymize web surfing. Anonymizers may be differentiated into several varieties. The destination server (the server that ultimately satisfies the web request) receives requests from the anonymizing proxy server and thus does not receive information about the end user’s address. The requests are not anonymous to the anonymizing proxy server, however, and so a degree of trust is present between the proxy server and the user. Many proxy servers are funded through a continued advertising link to the user.
Access control: Some proxy servers implement a logon requirement. In large organizations, authorized users must log on to gain access to the web. The organization can thereby track usage to individuals. Some anonymizing proxy servers may forward data packets with header lines such as HTTP_VIA, HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR, or HTTP_FORWARDED, which may reveal the IP address of the client. Other anonymizing proxy servers, known as elite or high-anonymity proxies, make it appear that the proxy server is the client. A website could still suspect a proxy is being used if the client sends packets that include a cookie from a previous visit that did not use the high-anonymity proxy server. Clearing cookies, and possibly the cache, would solve this problem.
QA geotargeted advertising[edit]
Advertisers use proxy servers for validating, checking and quality assurance of geotargeted ads. A geotargeting ad server checks the request source IP address and uses a geo-IP database to determine the geographic source of requests.[14] Using a proxy server that is physically located inside a specific country or a city gives advertisers the ability to test geotargeted ads.
Security[edit]
A proxy can keep the internal network structure of a company secret by using network address translation, which can help the security of the internal network.[15] This makes requests from machines and users on the local network anonymous. Proxies can also be combined with firewalls.
An incorrectly configured proxy can provide access to a network otherwise isolated from the Internet.[4]
Cross-domain resources[edit]
Proxies allow web sites to make web requests to externally hosted resources (e.g. images, music files, etc.) when cross-domain restrictions prohibit the web site from linking directly to the outside domains. Proxies also allow the browser to make web requests to externally hosted content on behalf of a website when cross-domain restrictions (in place to protect websites from the likes of data theft) prohibit the browser from directly accessing the outside domains.
Malicious usages[edit]
Secondary market brokers[edit]
Secondary market brokers use web proxy servers to circumvent restrictions on online purchase of limited products such as limited sneakers[16] or tickets.
Implementations of proxies[edit]
Web proxy servers[edit]
Web proxies forward HTTP requests. The request from the client is the same as a regular HTTP request except the full URL is passed, instead of just the path.[17]
GET https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Proxy_server HTTP/1.1 Proxy-Authorization: Basic encoded-credentials Accept: text/html
This request is sent to the proxy server, the proxy makes the request specified and returns the response.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: text/html; charset UTF-8
Some web proxies allow the HTTP CONNECT method to set up forwarding of arbitrary data through the connection; a common policy is to only forward port 443 to allow HTTPS traffic.
Examples of web proxy servers include Apache (with mod_proxy or Traffic Server), HAProxy, IIS configured as proxy (e.g., with Application Request Routing), Nginx, Privoxy, Squid, Varnish (reverse proxy only), WinGate, Ziproxy, Tinyproxy, RabbIT and Polipo.
For clients, the problem of complex or multiple proxy-servers is solved by a client-server Proxy auto-config protocol (PAC file).
SOCKS proxy[edit]
SOCKS also forwards arbitrary data after a connection phase, and is similar to HTTP CONNECT in web proxies.
Transparent proxy[edit]
Also known as an intercepting proxy, inline proxy, or forced proxy, a transparent proxy intercepts normal application layer communication without requiring any special client configuration. Clients need not be aware of the existence of the proxy. A transparent proxy is normally located between the client and the Internet, with the proxy performing some of the functions of a gateway or router.[18]
RFC 2616 (Hypertext Transfer Protocol—HTTP/1.1) offers standard definitions:
«A ‘transparent proxy’ is a proxy that does not modify the request or response beyond what is required for proxy authentication and identification». «A ‘non-transparent proxy’ is a proxy that modifies the request or response in order to provide some added service to the user agent, such as group annotation services, media type transformation, protocol reduction, or anonymity filtering».
TCP Intercept is a traffic filtering security feature that protects TCP servers from TCP SYN flood attacks, which are a type of denial-of-service attack. TCP Intercept is available for IP traffic only.
In 2009 a security flaw in the way that transparent proxies operate was published by Robert Auger,[19] and the Computer Emergency Response Team issued an advisory listing dozens of affected transparent and intercepting proxy servers.[20]
Purpose[edit]
Intercepting proxies are commonly used in businesses to enforce acceptable use policy, and to ease administrative overheads since no client browser configuration is required. This second reason however is mitigated by features such as Active Directory group policy, or DHCP and automatic proxy detection.
Intercepting proxies are also commonly used by ISPs in some countries to save upstream bandwidth and improve customer response times by caching. This is more common in countries where bandwidth is more limited (e.g. island nations) or must be paid for.
Issues[edit]
The diversion/interception of a TCP connection creates several issues. First, the original destination IP and port must somehow be communicated to the proxy. This is not always possible (e.g., where the gateway and proxy reside on different hosts). There is a class of cross-site attacks that depend on certain behavior of intercepting proxies that do not check or have access to information about the original (intercepted) destination. This problem may be resolved by using an integrated packet-level and application level appliance or software which is then able to communicate this information between the packet handler and the proxy.
Intercepting also creates problems for HTTP authentication, especially connection-oriented authentication such as NTLM, as the client browser believes it is talking to a server rather than a proxy. This can cause problems where an intercepting proxy requires authentication, then the user connects to a site that also requires authentication.
Finally, intercepting connections can cause problems for HTTP caches, as some requests and responses become uncacheable by a shared cache.
Implementation methods[edit]
In integrated firewall/proxy servers where the router/firewall is on the same host as the proxy, communicating original destination information can be done by any method, for example Microsoft TMG or WinGate.
Interception can also be performed using Cisco’s WCCP (Web Cache Control Protocol). This proprietary protocol resides on the router and is configured from the cache, allowing the cache to determine what ports and traffic is sent to it via transparent redirection from the router. This redirection can occur in one of two ways: GRE tunneling (OSI Layer 3) or MAC rewrites (OSI Layer 2).
Once traffic reaches the proxy machine itself interception is commonly performed with NAT (Network Address Translation). Such setups are invisible to the client browser, but leave the proxy visible to the web server and other devices on the internet side of the proxy. Recent Linux and some BSD releases provide TPROXY (transparent proxy) which performs IP-level (OSI Layer 3) transparent interception and spoofing of outbound traffic, hiding the proxy IP address from other network devices.
Detection[edit]
Several methods may be used to detect the presence of an intercepting proxy server:
- By comparing the client’s external IP address to the address seen by an external web server, or sometimes by examining the HTTP headers received by a server. A number of sites have been created to address this issue, by reporting the user’s IP address as seen by the site back to the user on a web page. Google also returns the IP address as seen by the page if the user searches for «IP».
- By comparing the result of online IP checkers when accessed using HTTPS vs HTTP, as most intercepting proxies do not intercept SSL. If there is suspicion of SSL being intercepted, one can examine the certificate associated with any secure web site, the root certificate should indicate whether it was issued for the purpose of intercepting.
- By comparing the sequence of network hops reported by a tool such as traceroute for a proxied protocol such as HTTP (port 80) with that for a non-proxied protocol such as SMTP (port 25).[21]
- By attempting to make a connection to an IP address at which there is known to be no server. The proxy will accept the connection and then attempt to proxy it on. When the proxy finds no server to accept the connection it may return an error message or simply close the connection to the client. This difference in behavior is simple to detect. For example, most web browsers will generate a browser created error page in the case where they cannot connect to an HTTP server but will return a different error in the case where the connection is accepted and then closed.[22]
- By serving the end-user specially programmed Adobe Flash SWF applications or Sun Java applets that send HTTP calls back to their server.
CGI proxy[edit]
A CGI web proxy accepts target URLs using a Web form in the user’s browser window, processes the request, and returns the results to the user’s browser. Consequently, it can be used on a device or network that does not allow «true» proxy settings to be changed. The first recorded CGI proxy, named «rover» at the time but renamed in 1998 to «CGIProxy»,[23] was developed by American computer scientist James Marshall in early 1996 for an article in «Unix Review» by Rich Morin.[24]
The majority of CGI proxies are powered by one of CGIProxy (written in the Perl language), Glype (written in the PHP language), or PHProxy (written in the PHP language). As of April 2016, CGIProxy has received about 2 million downloads, Glype has received almost a million downloads,[25] whilst PHProxy still receives hundreds of downloads per week.[26] Despite waning in popularity[27] due to VPNs and other privacy methods, as of September 2021 there are still a few hundred CGI proxies online.[28]
Some CGI proxies were set up for purposes such as making websites more accessible to disabled people, but have since been shut down due to excessive traffic, usually caused by a third party advertising the service as a means to bypass local filtering. Since many of these users don’t care about the collateral damage they are causing, it became necessary for organizations to hide their proxies, disclosing the URLs only to those who take the trouble to contact the organization and demonstrate a genuine need.[29]
Suffix proxy[edit]
A suffix proxy allows a user to access web content by appending the name of the proxy server to the URL of the requested content (e.g. «en.wikipedia.org.SuffixProxy.com«). Suffix proxy servers are easier to use than regular proxy servers but they do not offer high levels of anonymity and their primary use is for bypassing web filters. However, this is rarely used due to more advanced web filters.
Tor onion proxy software[edit]
Tor is a system intended to provide online anonymity.[30] Tor client software routes Internet traffic through a worldwide volunteer network of servers for concealing a user’s computer location or usage from someone conducting network surveillance or traffic analysis. Using Tor makes tracing Internet activity more difficult,[30] and is intended to protect users’ personal freedom and their online privacy.
«Onion routing» refers to the layered nature of the encryption service: The original data are encrypted and re-encrypted multiple times, then sent through successive Tor relays, each one of which decrypts a «layer» of encryption before passing the data on to the next relay and ultimately the destination. This reduces the possibility of the original data being unscrambled or understood in transit.[31]
I2P anonymous proxy[edit]
The I2P anonymous network (‘I2P’) is a proxy network aiming at online anonymity. It implements garlic routing, which is an enhancement of Tor’s onion routing. I2P is fully distributed and works by encrypting all communications in various layers and relaying them through a network of routers run by volunteers in various locations. By keeping the source of the information hidden, I2P offers censorship resistance. The goals of I2P are to protect users’ personal freedom, privacy, and ability to conduct confidential business.
Each user of I2P runs an I2P router on their computer (node). The I2P router takes care of finding other peers and building anonymizing tunnels through them. I2P provides proxies for all protocols (HTTP, IRC, SOCKS, …).
Comparison to network address translators[edit]
The proxy concept refers to a layer 7 application in the OSI reference model. Network address translation (NAT) is similar to a proxy but operates in layer 3.
In the client configuration of layer-3 NAT, configuring the gateway is sufficient. However, for the client configuration of a layer 7 proxy, the destination of the packets that the client generates must always be the proxy server (layer 7), then the proxy server reads each packet and finds out the true destination.
Because NAT operates at layer-3, it is less resource-intensive than the layer-7 proxy, but also less flexible. As we compare these two technologies, we might encounter a terminology known as ‘transparent firewall’. Transparent firewall means that the proxy uses the layer-7 proxy advantages without the knowledge of the client. The client presumes that the gateway is a NAT in layer 3, and it does not have any idea about the inside of the packet, but through this method, the layer-3 packets are sent to the layer-7 proxy for investigation.
DNS proxy[edit]
A DNS proxy server takes DNS queries from a (usually local) network and forwards them to an Internet Domain Name Server. It may also cache DNS records.
Proxifiers[edit]
Some client programs «SOCKS-ify» requests,[32] which allows adaptation of any networked software to connect to external networks via certain types of proxy servers (mostly SOCKS).
Residential proxy[edit]
A residential proxy is an intermediary that uses a real IP address provided by an Internet Service Provider (ISP) with physical devices such as mobiles and computers of end-users. Instead of connecting directly to a server, residential proxy users connect to the target through residential IP addresses. The target then identifies them as organic internet users. It does not let any tracking tool identify the reallocation of the user. Any residential proxy can send any number of concurrent requests and IP addresses are directly related to a specific region.[33] Unlike regular residential proxies, which hide user’s real IP address behind another IP address, rotating residential proxies, also known as backconnect proxies, conceal user’s real IP address behind a pool of proxies. These proxies switch between themselves with every session or at regular intervals.[34]
See also[edit]
- InterPlanetary File System — makes proxy servers redundant
- Application firewall
- Captive portal
- Darknet
- Distributed Checksum Clearinghouse
- FreeProxy
- Internet privacy
- Proxy list
- SMTP proxy
- SOCKS an alternative firewall traversal protocol supported by many applications
- Web accelerator which discusses host-based HTTP acceleration
- Web cache
References[edit]
- ^ World-Wide Web Proxies, Ari Luotonen, April 1994
- ^ Shapiro, Marc (May 1986). Structure and Encapsulation in Distributed Systems: the Proxy Principle. 6th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS). Cambridge, MA, USA. pp. 198–204. inria-00444651.
- ^ «Proxy servers and tunneling». MDN Web Docs. Retrieved 6 December 2020.
- ^ a b Lyon, Gordon (2008). Nmap network scanning. US: Insecure. p. 270. ISBN 978-0-9799587-1-7.
- ^ «Forward and Reverse Proxies». httpd mod_proxy. Apache. Retrieved 20 December 2010.
- ^ a b «2010 Circumvention Tool Usage Report» (PDF). The Berkman Center for Internet & Society at Harvard University. October 2010.
- ^ «How to Check if Website is Down or Working Worldwide». Hostinger. 19 November 2019. Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- ^ «Using a Ninjaproxy to get through a filtered proxy». advanced filtering mechanics. TSNP. Archived from the original on 9 March 2016. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ Thomas, Keir (2006). Beginning Ubuntu Linux: From Novice to Professional. Apress. ISBN 978-1-59059-627-2.
A proxy server helps speed up Internet access by storing frequently accessed pages
- ^ I. Cooper; J. Dilley (June 2001). Known HTTP Proxy/Caching Problems. IETF. doi:10.17487/RFC3143. RFC 3143. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ^ «Layering». Performance Enhancing Proxies Intended to Mitigate Link-Related Degradations. IETF. June 2001. p. 4. sec. 2.1. doi:10.17487/RFC3135. RFC 3135. Retrieved 21 February 2014.
- ^ Durieux, T.; Hamadi, Y.; Monperrus, M. (2018). «Fully Automated HTML and JavaScript Rewriting for Constructing a Self-Healing Web Proxy». 2018 IEEE 29th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE). 2018 IEEE 29th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering (ISSRE). pp. 1–12. arXiv:1803.08725. doi:10.1109/ISSRE.2018.00012. ISBN 978-1-5386-8321-7. S2CID 4268784.
- ^ Zhang, Xiaoyi; Ross, Anne Spencer; Caspi, Anat; Fogarty, James; Wobbrock, Jacob O. (2017). «Interaction Proxies for Runtime Repair and Enhancement of Mobile Application Accessibility». Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems. pp. 6024–6037. doi:10.1145/3025453.3025846. ISBN 9781450346559. S2CID 20937177.
- ^ «Hot Tactics For Geo-Targeted Ads on Google & Bing». October 2013. Retrieved 7 February 2014.
- ^ «Firewall and Proxy Server HOWTO». tldp.org. Retrieved 4 September 2011.
The proxy server is, above all, a security device.
- ^ «Sneaker Bot Supreme Proxy». GeoSurf. Retrieved 24 September 2017.
- ^ «absolute-form». HTTP/1.1 Message Syntax and Routing. IETF. June 2014. p. 41. sec. 5.3.2. doi:10.17487/RFC7230. RFC 7230. Retrieved 4 November 2017.
a client MUST send the target URI in absolute-form as the request-target
- ^ «Transparent Proxy Definition». ukproxyserver.org. 1 February 2011. Archived from the original on 1 March 2013. Retrieved 14 February 2013.
- ^ «Socket Capable Browser Plugins Result in Transparent Proxy Abuse». The Security Practice. 9 March 2009. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- ^ «Vulnerability Note VU#435052». US CERT. 23 February 2009. Retrieved 14 August 2010.
- ^ «Subversion Dev: Transparent Proxy detection (was Re: Introduction_». Tracetop.sourceforge.net. Retrieved 16 November 2014.
- ^ Wessels, Duane (2004). Squid The Definitive Guide. O’Reilly. pp. 130. ISBN 978-0-596-00162-9.
- ^ Marshall, James. «CGIProxy». Retrieved 12 November 2018.
- ^ «The Limits of Control». June 1996. Retrieved 12 November 2018.
- ^ «Glype® Proxy Script». glype.com. Archived from the original on 3 January 2013. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ^ «PHProxy». SourceForge.
- ^ «Google Trends». Google Trends.
- ^ «Proxy Stats :: Get Proxi.es». getproxi.es. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- ^ Estrada-Jiménez, José (March 2017). «Online advertising: Analysis of privacy threats and protection approaches». Computer Communications. 100: 32–51. doi:10.1016/j.comcom.2016.12.016. hdl:2117/99742.
- ^ a b Glater, Jonathan (25 January 2006). «Privacy for People Who Don’t Show Their Navels». The New York Times. Retrieved 4 August 2011.
- ^ The Tor Project. «Tor: anonymity online». Retrieved 9 January 2011.
- ^ Zwicky, Elizabeth D.; Cooper, Simon; Chapman, D. Brent (2000). Building Internet Firewalls (2nd ed.). p. 235. ISBN 978-1-56592-871-8.
- ^ Smith, Vincent (2019). Go Web Scraping Quick Start Guide: Implement the power of Go to scrape and crawl data from the web. Packt Publishing Ltd. ISBN 978-1-78961-294-3.
- ^ Keenan, James. «What are Residential Proxies?». Smartproxy.com. Retrieved 26 December 2021.
External links[edit]
- Proxy software and scripts at Curlie
- Free web-based proxy services at Curlie
- Free http proxy servers at Curlie
Прокси-сервер (от англ. proxy — «представитель, уполномоченный») — сервер (комплекс программ) в компьютерных сетях, позволяющий клиентам выполнять косвенные запросы к другим сетевым службам. Сначала клиент подключается к прокси-серверу и запрашивает какой-либо ресурс (например, e-mail), расположенный на другом сервере. Затем прокси-сервер либо подключается к указанному серверу и получает ресурс у него, либо возвращает ресурс из собственного кэша (в случаях, если прокси имеет свой кэш). В некоторых случаях запрос клиента или ответ сервера может быть изменён прокси-сервером в определённых целях. Прокси-сервер позволяет защищать компьютер клиента от некоторых сетевых атак и помогает сохранять анонимность клиента.
Все значения слова «прокси-сервер»
-
Выбрать страну проживания можно с помощью анонимных прокси-серверов.
-
Однако большинство прокси-серверов используются не для аутентификации, а для кэширования страниц.
-
Имя или IP-адрес прокси-сервера можно занести в настройки браузера.
- (все предложения)
- браузер
- сервак
- сервер
- ретранслятор
- аудиофайл
- (ещё синонимы…)
-
1
proxy server
сервер-посредник, сервер-представитель, -сервер, прокси-сервер, прокси
Англо-русский толковый словарь терминов и сокращений по ВТ, Интернету и программированию. > proxy server
-
2
proxy server
- сервер-посредник
- прокси-сервер
- прокси сервер
прокси-сервер
В компаниях, пользующихся Интернетом, прокси-серверы выступают в качестве посредников между пользователями рабочих станций и Интернетом. Они обеспечивают безопасность, администрирование и службы кэширования. Прокси-сервер, связанный с сервером шлюза или его частью, эффективно отделяет внутреннюю сеть предприятия от внешней сети и локального межсетевого экрана. От вторжений извне предприятие защищает сервер межсетевого экрана.
Прокси-сервер получает запросы к службам Интернета (например, запросы веб страниц) от пользователей. Если прокси-сервер также выполняет функцию сервера кэширования, он производит поиск уже загруженных веб-страниц в своем локальном кэше. Если он находит искомую страницу, она отправляется пользователю без перенаправления запроса в Интернет. Если страница не найдена в кэше, прокси-сервер выступает в качестве клиента от имени пользователя и, используя свой собственный IP-адрес, направляет запрос другому серверу через Интернет. По получении запрашиваемой страницы прокси-сервер пересылает ее пользователю, от которого поступил первоначальный запрос.
[ http://www.alltso.ru/publ/glossarij_setevoe_videonabljudenie_terminy/1-1-0-34]Тематики
- информационные технологии в целом
EN
- proxy server
сервер-посредник
proxy-сервер
Компьютер или работающее на нем программное обеспечение, образующие барьер между двумя сетями, одна из которых закрыта для посторонних, а другая общедоступна. Изолирует интрасеть, выступая в Интернете в роли ее представителя. Главная обязанность – передавать запросы клиентов сети узлам Интернет и возвращать требуемую информацию клиенту.
[ http://www.morepc.ru/dict/]Тематики
- информационные технологии в целом
EN
- proxy server
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > proxy server
-
3
proxy server
Большой англо-русский и русско-английский словарь > proxy server
-
4
proxy server
Универсальный англо-русский словарь > proxy server
-
5
proxy server
1) proxy-сервер, брандмауэр
2) посреднический сервер; промежуточный сервер
English-Russian dictionary of computer science and programming > proxy server
-
6
Proxy Server
English-Russian electronics dictionary > Proxy Server
-
7
proxy server
сервер-посредник, сервер с программным обеспечением для кеширования и фильтрации пользовательской информации, проф. прокси-сервер
English-Russian electronics dictionary > proxy server
-
8
Proxy Server
The New English-Russian Dictionary of Radio-electronics > Proxy Server
-
9
proxy server
сервер-посредник, сервер с программным обеспечением для кэширования и фильтрации пользовательской информации, проф. прокси-сервер
The New English-Russian Dictionary of Radio-electronics > proxy server
-
10
Proxy Server
Англо-русский экономический словарь > Proxy Server
-
11
proxy server
English-Russian dictionary of technical terms > proxy server
-
12
proxy server
сервер-заместитель; сервер-посредник; уполномоченный сервер; сервер-представитель; прокси-сервер
English-Russian information technology > proxy server
-
13
Microsoft Proxy Server
English-Russian SQL Server dictionary > Microsoft Proxy Server
-
14
Trojan proxy server
Универсальный англо-русский словарь > Trojan proxy server
-
15
cache/proxy server
Универсальный англо-русский словарь > cache/proxy server
-
16
proxy-сервер
Большой англо-русский и русско-английский словарь > proxy-сервер
-
17
server
The New English-Russian Dictionary of Radio-electronics > server
-
18
Server
English-Russian electronics dictionary > Server
-
19
Server
The New English-Russian Dictionary of Radio-electronics > Server
-
20
proxy service
Англо-русский толковый словарь терминов и сокращений по ВТ, Интернету и программированию. > proxy service
См. также в других словарях:
-
Proxy Server — [dt. »Stellvertreter Server«], ein Dienst im Internet (bzw. der Rechner, auf dem die entsprechende Software läuft), der zwischen einen Einzelrechner und das Gesamtnetz geschaltet ist. Fordert eine Person an ihrem Rechner ein Dokument aus dem… … Universal-Lexikon
-
proxy server — noun (computing) An intermediate server via which client devices can access other servers • • • Main Entry: ↑proxy * * * proxy server UK US noun [countable] [singular proxy server … Useful english dictionary
-
Proxy-Server — werden oftmals von Internet Providern betrieben, um Webseiten, die häufig abgerufen werden, zwischenzuspeichern. Wenn erneut ein Abruf der selben Webseite von einem Kunden des Internet Providers erfolgt, prüft der Proxy Server, ob die Daten der… … SEO Wörterbuch
-
Proxy server — For Wikipedia s policy on editing from open proxies, please see Wikipedia:Open proxies. Communication between two computers (shown in grey) connected through a third computer (shown in red) acting as a proxy. In … Wikipedia
-
Proxy-Server — Ein Proxy (von engl. „proxy representative“ = Stellvertreter, bzw. lat. „proximus“ = der Nächste) arbeitet als Vermittler, der auf der einen Seite Anfragen entgegennimmt, um dann über seine eigene Adresse eine Verbindung zur anderen Seite… … Deutsch Wikipedia
-
Proxy Server — Ein Proxy (von engl. „proxy representative“ = Stellvertreter, bzw. lat. „proximus“ = der Nächste) arbeitet als Vermittler, der auf der einen Seite Anfragen entgegennimmt, um dann über seine eigene Adresse eine Verbindung zur anderen Seite… … Deutsch Wikipedia
-
proxy server — A software package running on a server positioned between an internal network and the Internet. The proxy server filters all outgoing connections so that they appear to be coming from the same machine, in an attempt to conceal the underlying… … Dictionary of networking
-
proxy server — UK / US noun [countable] Word forms proxy server : singular proxy server plural proxy servers computing a computer system that allows users to go to popular websites more quickly, by storing pages that are often asked for or have been recently… … English dictionary
-
proxy server — įgaliotasis serveris statusas T sritis informatika apibrėžtis ↑Serveris, esantis tarp kompiuterio arba ↑vietinio tinklo ir išorinio tinklo. Per jį gali eiti visi ↑kliento (↑vietinio tinklo) ryšiai su išoriniu pasauliu. Kai klientas nori užmegzti… … Enciklopedinis kompiuterijos žodynas
-
proxy server — įgaliotoji programa statusas T sritis informatika apibrėžtis Programa, atliekanti tarpininko vaidmenį tarp tinklo (interneto) ir kompiuteryje esančių programų. Per ją gali eiti visi ↑kliento ryšiai su išoriniu pasauliu. Kai klientas (tiksliau –… … Enciklopedinis kompiuterijos žodynas
-
proxy server — /ˈprɒksi sɜvə/ (say proksee servuh) noun Internet a server which acts as a buffer between the user and the internet, performing a range of functions such as storing frequently used data in a cache to speed access, imposing restrictions on access… …
Что такое прокси-сервер
Прокси-сервер, или
просто прокси – это компьютер, выполняющий роль посредника между пользователем и целевым сервером. Сначала клиент подключается к прокси-серверу и запрашивает необходимый ресурс, расположенный на другом сервере. Например, почту или html-страницу. Затем прокси либо подключается к указанному серверу и получает у него ресурс, либо возвращает ресурс из собственного кэша.
Компании используют прокси для обеспечения безопасности, повышения производительности сети, доступа к «удаленным» ресурсам. Частные лица применяют прокси для анонимизации трафика или обхода ограничений доступа.
Когда речь заходит о
прокси, обычно подразумевается прямой прокси-сервер. Представим, что мы делаем запрос, например, пытаемся перейти на GitHub – вводим
URL, нажимаем Enter. Прокси не подключает нас к GitHub напрямую, а перехватывает соединение и обновляет содержание запроса, удаляя входящий IP и изменяя заголовок. В результате GitHub считает, что запрос пришел с другого
компьютера, и отправляет нужные данные не нам, а прокси-серверу. Прокси принимает информацию GitHub, проверяет и отправляет данные нашему компьютеру.
Как применяются прокси-серверы
Распространенные варианты использования прокси:
- повышение безопасности сети с помощью шифрования запросов;
- предотвращение перехвата конфиденциальной информации;
- блокировка вредоносных сайтов и рекламы;
- кэширование сайтов для экономии трафика;
- контроль использования сетевого канала;
- блокировка доменов;
- мониторинг и регистрация веб-запросов;
- тестирование веб-ресурсов при заходе с различных IP.
Свои варианты вы можете предложить в комментариях к публикации.
Какие бывают типы прокси-серверов
Прозрачный прокси – самый простой вид, в браузере даже не прописываются настройки прокси-сервера. Прозрачный прокси просто перехватывает идущий HTTP-трафик. У пользователя создается ощущение, что он работает в интернете без прокси-сервера. Пример использования: фильтрация развлекательных веб-сайтов в сети образовательных учреждений.
Анонимный прокси никогда не передают IP-адрес клиента на целевой ресурс. Хороший вариант, если вы не хотите,
чтобы таргетированная реклама следила за вами или вашим местоположением. Прокси высокой анонимности не передает ни IP-адрес, ни личные данные и даже не идентифицирует себя как прокси. В процессе работы IP-адрес периодически меняется – это позволяет обеспечить максимальную конфиденциальность. Браузер TOR использует этот тип прокси-сервера. Поскольку IP меняется, чрезвычайно трудно отследить источник запросов.
Искажающий (distorting) прокси работает
аналогично анонимному, но передает заведомо ложный IP-адрес. Такой подход используется, чтобы обойти локальные ограничения доступа к контенту.
Резидентный (residential) прокси используют реальные (белые, статические) IP-адреса. Для серверов они выглядят
как обычные клиенты. Противоположность резидентного – data center прокси, имеющие IP-адреса, не привязанные
к реальному устройству. Облачные провайдеры имеют высокоскоростные интернет-соединения. Однако если на одном сервере размещено сотни прокси-серверов, все они будут иметь одинаковые IP-адреса.
Публичный (public) прокси – самый небезопасный и ненадежный. Могут «отвалиться» в любой
момент, уязвимы для хакерских атак. Найти списки бесплатных
публичных прокси не так уж сложно, но найти хороший публичный прокси – почти невозможно.
Частный (private) прокси может использоваться единовременно только одним клиентом, а перед использованием происходит проверка подлинности. Это более надежная версия публичного прокси. Частный прокси-сервер может быть прозрачным или иметь высокую анонимность, подобно вышеописанным собратьям, таким как резидентный или data center прокси.
Общий (shared) прокси – один из самых
дешевых видов прокси-серверов. Стоимость аренды сервера разделяется между клиентами, которые получают к нему одновременный доступ.
Ротационный (rotating) прокси для нового клиента выделяет новый IP-адрес. То есть один и тот же IP не используется более одного раза. Ротационный сервер
обеспечивает высокий уровень безопасности и конфиденциальности.
SSL-прокси работают
по принципу HTTPS-запросов – запросы
между клиентом и сервером защищены шифрованием.
Обратный (reverse) прокси предлагает совершенно другой
подход к проксированию. Здесь скрывается не IP-адрес клиента, а IP-адрес сервера, на который отправляется
запрос. Инструмент используется, чтобы контролировать доступ к серверу и ограничивать
неконтролируемый доступ к базе данных, а также для снижения трафика за счет кэширования информации.
Где искать прокси
Большинство сервисов прокси предлагают комбинации вышеописанных типов. Можно обнаружить, что резидентные, высоко анонимные и SSL-прокси объединены в один сервис. Список сервисов, на которых можно выбрать подходящий вариант:
- https://smartproxy.com/
- https://www.megaproxy.com/
- https://whoer.net/webproxy
- https://www.proxysite.com/
- https://hide.me/en/proxy
- https://www.kproxy.com/
- https://www.vpnbook.com/webproxy
В чем разница между прокси и VPN
Главное отличие прокси от VPN заключается в том, что VPN защищает весь сетевой трафик, а
прокси – только интернет-трафик. Прокси передает запросы, действуя как посредник,
а VPN туннелирует всю сетевую активность до уровня операционной системы.
Компании используют VPN, чтобы дать доступ сотрудникам к корпоративным
ресурсам, не беспокоясь о том, что трафик будет перехвачен или задамплен
провайдером. Если он получит историю использования, в ней будет видно только
то, что вы подключены к VPN. Ничего о трафике узнать нельзя.
Несмотря на все
преимущества, у VPN в сравнении с прокси есть недостатки:
- VPN дороже;
- соединение обычно происходит медленнее.
Для многих задач уровень безопасности VPN может оказаться избыточным. Если вы
просто хотите замаскировать действия в приложении, стоит
рассмотреть прокси-сервер.
Как настроить простой прокси-сервер
Создать собственный прокси-сервер проще, чем, кажется. Прокси-сервер может располагаться где угодно, им может стать даже домашний компьютер. На сервере Linux можно установить Squid и задать необходимые настройки. Можно блокировать
определенные веб-сайты или требовать аутентификацию, прежде чем клиент подключится к прокси-серверу (пошаговое руководство по настройке Squid).
В Windows и Mac есть возможность создать прокси-сервер с помощью Python и Google
App Engine, но придется немного
заплатить. Настройка сервера незначительно сложнее, чем в Linux.
Как подключиться к существующему прокси-серверу
Если вы знаете IP-адрес и номер порта прокси, подключиться будет несложно. Нужно зайти
в настройки сети, далее в раздел прокси, а после ввести информацию о сервере.
Заключение
Использование прокси оправдано, если необходимо скрыть или защитить информацию. Выше мы рассмотрели список задач, решаемых с помощью прокси. Как мы увидели, в использовании прокси есть преимущества:
- безопасность и конфиденциальность данных в интернете;
- возможность обойти ограничения, связанные с геолокацией;
- возможность повысить производительность сети;
- возможность контролировать доступ к сайтам.
Но есть и недостатки:
- запросы могут возвращаться медленнее, чем при прямом обращении;
- не все прокси шифруют данные, к выбору прокси нужно относиться внимательно;
- бесплатные и дешевые прокси могут быть подвергнуты атаке, в результате чего данные могут перехватываться мошенниками;
- вся информация всегда проходит через третью сторону, которая может управляться кем угодно.
Если вам интересна тема информационной безопасности, в Библиотеке программиста есть множество публикаций на эту тему, например:
- «Я тебя по IP вычислю»: как хакеры рассекречивают звенья цепи Tor
- Как стать специалистом по информационной безопасности
- Что такое кибербезопасность и почему за этой профессией будущее?
Добрый день, друзья. Что такое прокси сервер и зачем он нужен? Прокси-сервер (ПС) — это часть оборудования, которое перехватывает и управляет трафиком между двумя устройствами, сетями или протоколами. Прокси — это шлюзы, которые действуют как посредники между вашим ПК и веб-сайтами и интернет-сервисами, которые вы используете. Они могут действовать как брандмауэры, фильтры или кэши и облегчать общие сетевые подключения.
Это общее определение ПС также известного как прямой прокси-сервер. На данный момент имеется много вариантов ПС, каждый из которых имеет разные функции, все они выполняют важную задачу представления вас (выступая в качестве вашего прокси-сервера) при работе в Интернете.
Что делает прокси-сервер?
ПС передает трафик между вашим устройством и Интернетом, предотвращая прямой контакт вашего браузера с посещаемыми вами сайтами. Ваши веб-запросы сначала проходят через ПС. После этого он отсылает ваш запрос на соответствующий веб-сервер и перенаправляет ответ на ваше устройство.
Выступая как посредник, ПС помогают защитить вашу конфиденциальность и повысить безопасность присутствия пользователя в сети. Другие полезные функции ПС, следующие:
- Возможности брандмауэра и веб-фильтра: у вас есть возможность ограничить доступ к определенным ресурсам и защитить свою сеть от хакеров.
- Общие сетевые подключения: вы можете подключить несколько устройств к сети.
- Кэш данных: вы можете увеличить скорость просмотра, сохраняя копии веб-страниц.
Как функционирует прокси-сервер?
ПС отсылает ваши запросы в глобальную сеть соответствующим адресатам, затем объединяет ответы и возвращает их вам. При использовании прокси-сервера единственной точкой контакта между локальной сетью вашего устройства и посещаемыми вами веб-сайтами является сам ПС.
Все ПС применяют IP вашего ПК. IP-адрес действует как почтовый адрес для вашего компьютера или устройства. Точно так же, как почта доставляется на ваш физический домашний адрес, интернет-информация возвращается на ваш уникальный IP, чтобы обеспечить передачу данных в нужное место.
Если вы подсоединяетесь к интернету без ПС, ваш IP раскрывается и может быть виден veb-серверам. По сути, очень легко узнать собственный IP-адрес, что может привести к нарушениям безопасности и прочим сбоям, связанным с идентификацией. Интернет-прокси также имеет IP, его также можно применять, чтобы не выдавать свой действительный IP.
Шаг 1. Ваши веб-запросы отправляются с вашего IP на ПС. Шаг 2. ПС отсылает ваш трафик на ресурс, на который у вас есть желание войти, применяя иной IP. Шаг 3. Ответы веб-сайта отправляются обратно на прокси-сервер. Шаг 4: ПС возвращает вам запрошенные данные без прямой связи veb-ресурса с вашим устройством.
Veb-ПС может маскировать ваш IP, что затрудняет отслеживание вашего физического местоположения веб-сервером. Но, маскировка вашего IP не проводит шифрование трафика, а это значит, что ваши запросы данных, включая имена пользователей, пароли и другие данные учетной записи, не защищены и не скрыты.
Конфигурация и установка
Как в Windows, так и в Mac ваш компьютер дает вам возможность настроить прокси-сервер. Часто в настройках прокси ваша операционная система может автоматически определять список доступных прокси-серверов. Однако, также можно ввести оригинальный IP и № порта ПС. Эта информация должна быть предоставлена вам вашим провайдером, если вы используете частный или коммерческий прокси-сервер. Подробнее, как настроить мобильные прокси можно узнать по ссылке.
Что такое пересылающие прокси?
ПС пересылки отправляют исходящие запросы от имени конечного пользователя или сети. Затем, прямой прокси-сервер получает ответы на эти запросы и возвращает их прокси-пользователю. Прокси-серверы пересылки могут быть настроены для проверки или фильтрации интернет-трафика и обработки запросов на основе определенных критериев. Например, некоторые исходящие запросы могут быть заблокированы.
Что такое обратные прокси?
Обратные ПС получают запросы от клиентов от имени сервера или группы серверов, а затем при необходимости передают эти запросы на серверы. Это предотвращает прямой обмен данными с серверами и повышает производительность за счет балансировки нагрузки, когда входящий трафик распределяется по нескольким серверам, а не только по одному.
Типы прокси-серверов
Хотя все ПС могут представлять вас в сети, разные прокси-серверы выполняют эту задачу по-разному в соответствии с вашими конкретными потребностями.
Прозрачные прокси
Прозрачный прокси сообщает веб-серверу, что он является прокси, и сообщает ему его реальный IP-адрес, чтобы он раскрыл вашу личность веб-серверу. Прозрачные ПС не применяются в целях безопасности или конфиденциальности. Как правило, прозрачные прокси используются образовательными учреждениями, предприятиями и общедоступными сетями, такими как библиотеки, для фильтрации содержимого или использования кэша данных.
Искажение прокси
Спин-прокси предоставляет поддельный IP веб-серверу. При этом даже если он идентифицирует себя как ПС, поддельный адрес обеспечивает анонимность, но его реальное состоит в том, что он может ввести veb-сервер в заблуждение, при котором он думает, что пользователь находится где-то еще. Другими словами, искажающие ПС могут обойти ограничения контента на основе местоположения. Хотя искажающие ПС добавляют уровень безопасности, минус тут в том, что некоторые veb-ресурсы автоматически банят ваши подключения.
Анонимные прокси
Анонимный ПС спрячет ваш IP от посещаемых вами веб-страниц. Это помогает бороться с кражей личных данных и обеспечивает анонимный просмотр. При этом, анонимные прокси не идентифицируют себя как ПС, и некоторые страницы могут отказать им в доступе.
Высокоанонимные прокси
ПС с высокой анонимностью периодически меняет IP, который он передает веб-серверам посещаемых вами сайтов. Это затрудняет использование веб-страницами методов онлайн-отслеживания для отслеживания вашей активности в Интернете. Если вы беспокоитесь о кибербезопасности, то прокси с высокой анонимностью — лучшее решение. Прокси с высокой анонимностью также не показывает, что это прокси, действующий от вашего имени. Это гарантирует, что ваши цифровые следы будут скрыты, поэтому это наиболее безопасный ПС.
Но, хотя они обеспечивают некоторую безопасность, большая часть ПС не шифруют ваш веб-поток, а что значит, что вы до сих пор уязвимы для различных онлайн-угроз, таких как хакеры или вредоносное сайты. Поэтому, рекомендуется применять VPN, который обеспечивает гораздо большую защиту, особенно если вы хотите оставаться в безопасности в общедоступных сетях Wi-Fi.
Вывод: мы рассмотрели, что такое прокси сервер и зачем он нужен? Как видите, существуют различные виды ПС с различной степенью защиты и шифрованием данных. Поэтому, при использовании общественного Wi-Fi, как уже сказал, рекомендуется применять VPN. Успехов!
С уважением, Андрей Зимин 30.12.2022
Понравилась статья? Поделитесь с друзьями!
Люди порой не задумываются о том, как работает интернет и о тех опасностях, которые он в себе таит. Ежегодно мы видим растущие показатели статистики утечек данных пользователей. Покрытие интернета в мире растет, и соответственно растет и ваш риск попасть на какую-нибудь мошенническую схему, потеряв деньги с карточки через фишинговый сайт, передать свои данные злоумышленникам, подхватить компьютерный вирус и другие неприятности.
Обычной практикой для уважающих себя предприятий стало использование VPN (аббревиатура от Virtual Private Network — “виртуальная частная сеть”) и прокси-серверов для того, чтобы защитить своих сотрудников и компанию от утечки данных, вирусов, лучше контролировать рабочее время коллег.
В этой статье речь пойдет о том:
Что такое прокси-сервер?
Как работает прокси-сервер?
Типы прокси-серверов
Почему вам следует воспользоваться прокси-сервером?
Основные риски прокси-серверов
Заключение
FAQ
Что такое прокси-сервер?
Прокси-сервер, или просто прокси — это посредник между вами и сайтом на который вы хотите перейти. В переводе с английского proxy — это “доверенное лицо”. Таким образом, вы доверяете прокси, чтобы он мог вас безопасно соединить с желаемым для вас сайтом. Отправляя запрос с вашего компьютера на веб-ресурс, который вы хотите посетить, он попадает на прокси-сервер. Прокси обрабатывает его, может зашифровать или каким-либо другим образом преобразовать его и передать на IP-адрес сайта. Веб- сайт отправляет ответ прокси, который уже показывает вам данные со страницы.
Вы спросите: “Но почему я не могу связаться с нужным мне сайтом напрямую?” Прокси-сервера обладают широкой функциональностью. Если веб-ресурс популярен, то они могут кэшировать данные страниц и передавать данные клиенту (то есть вам) быстрее, чем обычным способом. Прокси могут сделать так, чтобы ваш IP-адрес не было видно. Так вы сможете безопасно открывать нужный вам сайт.
Прокси-сервера работают как своеобразные фаерволы, и брандмауэры, блокируя поступающий трафик на локальную сеть вашей организации например. Это позволяет защищать сотрудников от взаимодействия с вирусами и другим нежелательным контентом.
Прокси также позволяет вам сохранять анонимность в сети, обеспечивая конфиденциальность ваших данных, шифруя ваши запросы, передаваемые на сайты.
Как работает прокси-сервер?
Начнем с того, что у каждого компьютера в Интернете есть уникальный Internet protocol (IP). Сокращенно IP-адрес. С помощью него можно определить ваше физическое местоположение. Это как номер вашего дома в паспорте или в других документах. Или номер вашего почтового отделения, куда вам приходит почта. Сайт должен знать ваш IP-адрес, чтобы не ошибиться с “доставкой” информации.
У прокси-сервера также есть свой IP-адрес. И ваш компьютер тоже знает этот адрес. Когда вы обращаетесь с запросом к какой-либо странице, то вначале ваши данные попадают к прокси. Затем он перенаправляет ваш запрос на сервер сайта, который вы хотите открыть. Получает данные с сайта и передает вам. Таким образом вы видите в вашем браузере запрашиваемую страницу.
Прокси-сервер может зашифровать ваш запрос, изменить информацию, которую вы пересылаете. Даже при модификации ваших данных интересующий вас веб-ресурс передаст прокси нужную вам информацию.
У прокси-серверов множество возможностей по сохранению вашей конфиденциальности. Они могут изменить ваш IP-адрес при передаче данных на сайт. И вебсайт не будет знать о вашем месторасположении. Могут шифровать данные, чтобы посторонние не смогли прочитать их. Прокси может также блокировать доступ к различным ресурсам в сети путем установки ограничений для IP-адресов с определенных регионов или стран.
Почему вам следует воспользоваться прокси-сервером?
У прокси-серверов есть ряд преимуществ, на которые вам следует обратить внимание перед использованием:
Доступ из локальной сети в Интернет. Компьютеры организации используют прокси для перехода на внешние веб-ресурсы. Это в свою очередь дает свои преимущества, о которых мы поговорим ниже.
Высокая скорость передачи данных. Прокси может кэшировать данные, то есть делать копии данных популярных сайтов и сохранять их на серверах. Затем по запросу сервер выдает их пользователям. Таким образом снижается нагрузка на такие сайты, и ускоряется получение данных с веб-ресурса клиентом.
Также прокси-сервера способны сжимать данные с сайтов, загружая их с веб-страницы. Затем они передают вам информацию в сжатом виде. Прокси могут, например передавать информацию без “тяжелых” рекламных картинок и видео. Это делает использование интернет-ресурсов для вас более быстрым и удобным.
Конфиденциальность. Прокси-сервера могут отправлять на сайты вместо ваших данных свои. Таким образом, никто не будет знать наверняка, кто обращается на ту или иную страницу. Например, прокси будет показывать веб-ресурсу, что вы в Германии, хотя на самом деле отправляете запрос из Грузии.
Безопасность. Сервер может заблокировать входящий трафик с неизвестных, подозрительных сайтов. Это защитит ваш компьютер или локальную сеть всей организации от вирусов, фишинговых email’ов и других зловредных программ и схем. Кроме того, вы можете усилить вашу защиту с помощью VPN, который может зашифровать весь канал передачи данных.
Контроль. Полезная функция для контроля обучения или работы. Можно ограничивать или закрывать доступ к социальным сетям, развлекательным и другим сайтам, файловым хранилищам для студентов учебных заведений, курсов или сотрудников организаций. Таким образом, они не будут отвлекаться. Также можно отслеживать количество времени проведенного на тех или иных сайтах.
Получение доступа к заблокированным ресурсам. Нередко в Интернете сайты некоторых стран ограничивают или запрещают доступ для IP-адресов с других стран. Также власти некоторых стран запрещают своим гражданам пользоваться веб-ресурсами с других стран. Прокси может обходить два вышеуказанных ограничения сохраняя вашу анонимность.
Типы прокси-серверов
Прокси-сервера делятся на несколько основных типов: по степени использования, способу передачи данных и анонимности. А те в свою очередь делятся на определенные виды.
По степени использования
Публичные
Это бесплатные общедоступные прокси. Такие сервера считаются ненадежными, поскольку сайты могут отправить их в “черный список”, ваши данные могут попасть в чужие руки. Кроме того, публичные прокси работают нестабильно. Собственники могут закрыть их для пользователей в любой момент. Поэтому лучше воспользоваться услугами других прокси-серверов.
Закрытые
Такие сервера ограничивают доступ для посторонних, требуя аутентификацию. Есть такие виды закрытых прокси: общие и выделенные. Первыми могут пользоваться несколько человек в организации. Это удешевляет использование прокси-серверов. Вторыми всем заправляет только один сотрудник. Во втором случае повышается надежность и безопасность системы.
По способу передачи данных
HTTP-прокси
В Интернете это самый популярный вид прокси-серверов. Применяются для эффективной работы браузеров, и других программ, которые используют протокол передачи данных во всемирной паутине, HTTP (аббревиатура от Hypertext Transfer Protocol — “протокол гипертекстовой передачи”). Такие прокси нельзя назвать самыми надежными, поскольку они не шифруют данные пользователей. Чем часто пользуются злоумышленники в сети.
HTTPS-прокси
В данном случае прокси использует надежное SSL-соединение (аббревиатура от Secure Sockets Layer — “уровень защищенных сокетов”). Оно позволяет зашифровать ваши данные, когда вы обращаетесь к интернет-ресурсам. Это особенно актуально там, где вы оплачиваете покупки в интернете, делаете переводы с банковских карт. Таким образом, мошенники не смогут перехватить вашу личную информацию.
SOCKS-прокси
Что значит SOCKS? Расшифровывается это название как Sock-Et-S, или сетевой прокси протокол. Это один из наиболее передовых протоколов. Он пригоден для работы не только с интернет страницами, но и с другими приложениями. SOCKS передает от вас информацию в виде пакетов, не модифицируя при этом HTTP-заголовки. Этот прокси не выдает и себя, и ваш IP. Это позволяет вам переходить на сайты анонимно, легко и удобно.
FTP-прокси
Такие прокси-сервера работают с файловыми менеджерами, с FTP-протоколами, что помогает вам получить доступ к файлам в сети. Отметим, что такой прокси работает в основном с FTP-клиентами.
По анонимности
Прозрачные
Судя по названию, такие прокси-серверы раскрывают всю информацию и о себе (показывая, что они прокси), и о пользователе. Характеризуется этот сервер удобством настройки. Его можно использовать для кэширования и фильтрации данных с сайтов. Это актуально там, где наблюдается ограниченная пропускная способность интернета, а желающих им попользоваться много. Вместо новой загрузки сайта, когда соединение перегружено, прокси кеширует информацию с ресурса и выдает ее пользователям по их запросу.
Анонимные (обычные)
Анонимные сервера показывают сети, что они прокси, но информацию о клиенте видоизменяют. Они это делают через подмену HTTP-заголовков и демонстрацию своего адреса вместо IP-адреса пользователя. Иногда ресурсы могут заблокировать прокси, но это может случиться крайне редко.
Искажающие
Эти виртуальные серверы не скрываются от сайтов. Хотя такие прокси дают искаженную информацию о пользователе, используя подставные IP. Вебсайт думает, что к нему обратился реальный клиент, а не прокси-сервер. В таком случае возможно использование IP другого региона, страны. Таким образом вы можете обойти блокировки по географическому признаку.
Приватные (элитные)
Шифруют все. Запрашиваемый веб-ресурс не видит, что запрос исходит от прокси. И ваши данные также шифруют. Заменяя HTTP-заголовок, прокси не дают никакой информации о вас сайтам. Последние в свою очередь видят обычное пользовательское подключение. Веб-ресурсам в таком случае сложно отследить трафик и определить, кто к ним обратился.
Основные риски использования прокси-серверов
- Время. Прокси требует детального изучения, чтобы в них хорошо разобраться. Вам нужно будет потратить какое-то время, чтобы эффективно их использовать.
- Ненадежность бесплатных серверов. Здесь бесплатный “сыр” действительно в “мышеловке”. Бесплатные прокси не могут похвастаться хорошей аппаратурой, технической поддержкой. Многие из них не обеспечивают элементарного шифрования данных клиентов. Кроме того, собственники таких серверов могут и вовсе прекратить работу без предупреждения.
- Передача данных третьим лицам. Работая через прокси вы по сути передаете личную информацию посторонним организациям. Данные получают: ваш провайдер и запрашиваемые страницы. Теперь добавляется еще один участник, который получает доступ к вашему трафику. Нужно отдавать себе отчет в том, будет ли выбранный прокси шифровать ваши данные и хранить их в безопасном месте.
Этот риск можно разделить на две части:
- Сохранение данных в истории браузера. Во-первых, есть вероятность того, что прокси-сервер может сохранять ваши запросы на сайты и ваш IP-адрес в истории браузера в незашифрованном виде. В таком случае вам нужно будет проверить каких политик придерживается этот прокси. Во-вторых, прокси-сервер может передавать ваши данные третьим лицам, хотя вы стремились к конфиденциальности вашей информации.
- Отсутствие шифрования. Есть ли смысл использовать прокси без шифрования вашего трафика? Зачем тогда пользоваться услугами таких серверов? Злоумышленники с легкостью получат те данные, которые вы пересылаете: логины, пароли, ваш IP-адрес и другую информацию. Обязательно проверяйте наличие услуги шифрования у прокси, которым вы пользуетесь или планируете пользоваться. Это нужно для вашей безопасности и анонимности.
Заключение
Прокси-сервера остаются актуальной темой сегодня. Есть страны в которых цензура в интернете — это нормально. Как развитые страны, так и развивающиеся вводят свои правила пользования в сети. Не все хотят, чтобы вы посетили их сайт. Организации не собираются делиться своими данными, раскрывать себя и хотят, чтобы их сотрудники работали продуктивно и не отвлекались на лишнюю информацию. Как мы уже убедились, прокси-сервера с этими задачами справляются очень хорошо.
Даже для обычного пользователя прокси очень полезны, так как ускоряют доступ к сайтам, быстро загружая нужные страницы.
Хотя есть и недостатки. Ненадежность бесплатных серверов, которые могут ограничить доступ в любое время, не шифровать, а значит и не защищать вашу анонимность, продавать ваши данные. Можете ли вы гарантировать, что прокси не передаст вашу личную информацию третьим лицам? Вы уверены в надёжности шифрования ваших данных? Разбираться в характеристиках прокси-серверов можно долго, а вам быстрое и безопасное соединение нужно уже “на вчера”.
Таким образом, лучше доверить вашу безопасность экспертам, которые знают основные проблемы пользователей при выборе прокси. И самое главное: знают как решать их самым эффективным способом: безопасно, надежно, быстро.
Есть несколько основных критериев, по которым вы можете выбрать надежного поставщика прокси-сервиса:
- процент бесперебойной работы (должен максимально приближаться к 100%);
- качество технического обслуживания и поддержки;
- масштаб охвата сервиса в мире (чем больше стран и регионов, тем лучше);
- объем данных, которые собирают прокси-сервера (также чем больше, тем лучше);
- количество обрабатываемых запросов за 1 секунду (чем выше производительность, тем прокси эффективнее);
- работает ли в соответствии с GDPR (аббревиатура от General Data Protection Regulation — “Общее положение о защите данных”), CCPA (аббревиатура от Canadian Consumer Protection Act — “Канадский закон о защите прав потребителей”) и/или другими положениями о защите данных пользователей;
- уровень доверия среди различных институтов, организаций, учебных заведений.
Рынок прокси-сервисов развивается. Появляются новые и новые виды прокси и прокси сети для более устойчивой работы и вашего удобства, такие как: резидентные прокси, серверные прокси, ISP-прокси, мобильная прокси сеть и другие виды прокси-серверов.
Поэтому изучайте, узнавайте больше о прокси-серверах и о том, как тот или иной вид прокси поможет решить ваши задачи.
FAQ
Что такое прокси-сервер?
Прокси-сервер — это сервер-посредник между вами и тем веб-ресурсом на который вы хотите попасть.
Для чего используется прокси-сервер?
Основными целями использования прокси-серверов являются контроль, обеспечение безопасности, конфиденциальности в сети, устойчивого соединения. Предприятия могут контролировать своих сотрудников, учебные заведения студентов. Организации защищают локальную сеть от интернет-угроз. Вы также можете ускорять загрузку страниц и обходить блокировки определенных веб-ресурсов.
Является ли VPN прокси-сервером?
VPN — это виртуальный сервер, который путем шифрования защищает весь канал передачи данных и в локальной сети, и в интернете. Прокси работает только с интернет-трафиком.
Какие прокси-сервера могут использоваться на практике?
Множество видов и типов прокси работает в сети. Одним из наиболее распространенных является TOR Network, который обеспечивает конфиденциальность и защищает ваши данные в интернете.
Какие преимущества прокси-сервера?
Основные преимущества прокси:
- Обеспечение конфиденциальности данных пользователей
- Контроль использования интернета в рамках организации
- Обеспечение устойчивого и быстрого соединения в сети
- Шифрование запросов от пользователей
- Обход запретов на посещения ресурсов из других стран, регионов.